Author's posts
May 19 2012
On This Day In History May 19
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
May 19 is the 139th day of the year (140th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 226 days remaining until the end of the year.

On this day in 1935, T.E. Lawrence, better known as Lawrence of Arabia, dies from injuries sustained in a motorcycle accident near his home in Dorset, England.
Lieutenant Colonel Thomas Edward Lawrence, CB, DSO (16 August 1888 – 19 May 1935) was a British Army officer renowned especially for his liaison role during the Arab Revolt against Ottoman Turkish rule of 1916-18. The extraordinary breadth and variety of his activities and associations, and his ability to describe them vividly in writing, earned him international fame as Lawrence of Arabia, a title popularised by the 1962 film based on his First World War activities.
Lawrence was born illegitimately in Tremadog, Wales in August 1888 to Sir Thomas Chapman and Sarah Junner, a governess, who was herself illegitimate. Chapman left his wife to live with Sarah Junner, and they called themselves Mr and Mrs Lawrence. In the summer of 1896 the Lawrences moved to Oxford, where from 1907 to 1910 young Lawrence studied history at Jesus College, graduating with First Class Honours. He became a practising archaeologist in the Middle East, working with David George Hogarth and Leonard Woolley on various excavations. In January 1914, following the outbreak of the First World War, Lawrence was co-opted by the British military to undertake a military survey of the Negev Desert while doing archaeological research.
Lawrence’s public image was due in part to American journalist Lowell Thomas‘ sensationalised reportage of the revolt as well as to Lawrence’s autobiographical account Seven Pillars of Wisdom (1922).
At the outbreak of the First World War Lawrence was a university post-graduate researcher who had for years travelled extensively within the Ottoman Empire provinces of the Levant (Transjordan and Palestine) and Mesopotamia (Syria and Iraq) under his own name. As such he became known to the Turkish Interior Ministry authorities and their German technical advisors. Lawrence came into contact with the Ottoman-German technical advisers, travelling over the German-designed, built, and financed railways during the course of his researches.
Even if Lawrence had not volunteered, the British would probably have recruited him for his first-hand knowledge of Syria, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. He was eventually posted to Cairo on the Intelligence Staff of the GOC Middle East.
Contrary to later myth, it was neither Lawrence nor the Army that conceived a campaign of internal insurgency against the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East, but rather the Arab Bureau of Britain’s Foreign Office. The Arab Bureau had long felt it likely that a campaign instigated and financed by outside powers, supporting the breakaway-minded tribes and regional challengers to the Turkish government’s centralised rule of their empire, would pay great dividends in the diversion of effort that would be needed to meet such a challenge. The Arab Bureau had recognised the strategic value of what is today called the “asymmetry” of such conflict. The Ottoman authorities would have to devote from a hundred to a thousand times the resources to contain the threat of such an internal rebellion compared to the Allies’ cost of sponsoring it.
At that point in the Foreign Office’s thinking they were not considering the region as candidate territories for incorporation in the British Empire, but only as an extension of the range of British Imperial influence, and the weakening and destruction of a German ally, the Ottoman Empire.
During the war, Lawrence fought with Arab irregular troops under the command of Emir Faisal, a son of Sherif Hussein of Mecca, in extended guerrilla operations against the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. He persuaded the Arabs not to make a frontal assault on the Ottoman stronghold in Medina but allowed the Turkish army to tie up troops in the city garrison. The Arabs were then free to direct most of their attention to the Turks’ weak point, the Hejaz railway that supplied the garrison. This vastly expanded the battlefield and tied up even more Ottoman troops, who were then forced to protect the railway and repair the constant damage.
In 1917, Lawrence arranged a joint action with the Arab irregulars and forces under Auda Abu Tayi (until then in the employ of the Ottomans) against the strategically located but lightly defended town of Aqaba. On 6 July, after a surprise overland attack, Aqaba fell to Lawrence and the Arab forces. After Aqaba, Lawrence was promoted to major. Fortunately for Lawrence, the new commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, General Sir Edmund Allenby, agreed to his strategy for the revolt, stating after the war:
“I gave him a free hand. His cooperation was marked by the utmost loyalty, and I never had anything but praise for his work, which, indeed, was invaluable throughout the campaign.”
Lawrence now held a powerful position, as an adviser to Faisal and a person who had Allenby’s confidence.
The following year, Lawrence was involved in the capture of Damascus in the final weeks of the war and was promoted to lieutenant-colonel in 1918. In newly liberated Damascus-which he had envisioned as the capital of an Arab state-Lawrence was instrumental in establishing a provisional Arab government under Faisal. Faisal’s rule as king, however, came to an abrupt end in 1920, after the battle of Maysaloun, when the French Forces of General Gouraud under the command of General Mariano Goybet http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M… entered Damascus, breaking Lawrence’s dream of an independent Arabia.
As was his habit when traveling before the war, Lawrence adopted many local customs and traditions (many photographs show him in the desert wearing white Arab dishdasha and riding camels).
During the closing years of the war he sought, with mixed success, to convince his superiors in the British government that Arab independence was in their interests. The secret Sykes-Picot Agreement between France and Britain contradicted the promises of independence he had made to the Arabs and frustrated his work.
In 1918 he co-operated with war correspondent Lowell Thomas for a short period. During this time Thomas and his cameraman Harry Chase shot a great deal of film and many photographs, which Thomas used in a highly lucrative film that toured the world after the war.
Lawrence’s major work is Seven Pillars of Wisdom, an account of his war experiences. In 1919 he had been elected to a seven-year research fellowship at All Souls College, Oxford, providing him with support while he worked on the book. In addition to being a memoir of his experiences during the war, certain parts also serve as essays on military strategy, Arabian culture and geography, and other topics. Lawrence re-wrote Seven Pillars of Wisdom three times; once “blind” after he lost the manuscript while changing trains at Reading railway station.
The list of his alleged “embellishments” in Seven Pillars is long, though many such allegations have been disproved with time, most definitively in Jeremy Wilson‘s authorised biography. However Lawrence’s own notebooks refute his claim to have crossed the Sinai Peninsula from Aqaba to the Suez Canal in just 49 hours without any sleep. In reality this famous camel ride lasted for more than 70 hours and was interrupted by two long breaks for sleeping which Lawrence omitted when he wrote his book.
Lawrence acknowledged having been helped in the editing of the book by George Bernard Shaw. In the preface to Seven Pillars, Lawrence offered his “thanks to Mr. and Mrs. Bernard Shaw for countless suggestions of great value and diversity: and for all the present semicolons.”
The first public edition was published in 1926 as a high-priced private subscription edition, printed in London by Roy Manning Pike and Herbert John Hodgson, with illustrations by Eric Kennington, Augustus John, Paul Nash, Blair Hughes-Stanton and his wife Gertrude Hermes. Lawrence was afraid that the public would think that he would make a substantial income from the book, and he stated that it was written as a result of his war service. He vowed not to take any money from it, and indeed he did not, as the sale price was one third of the production costs. This left Lawrence in substantial debt.
At the age of 46, two months after leaving the service, Lawrence was fatally injured in an accident on his Brough Superior SS100 motorcycle in Dorset, close to his cottage, Clouds Hill, near Wareham. A dip in the road obstructed his view of two boys on their bicycles; he swerved to avoid them, lost control and was thrown over the handlebars. He died six days later on 19 May 1935. The spot is marked by a small memorial at the side of the road.
The circumstances of Lawrence’s death had far-reaching consequences. One of the doctors attending him was the neurosurgeon Hugh Cairns. He was profoundly affected by the incident, and consequently began a long study of what he saw as the unnecessary loss of life by motorcycle dispatch riders through head injuries. His research led to the use of crash helmets by both military and civilian motorcyclists.
Moreton Estate, which borders Bovington Camp, was owned by family cousins, the Frampton family. Lawrence had rented and later bought Clouds Hill from the Framptons. He had been a frequent visitor to their home, Okers Wood House, and had for years corresponded with Louisa Frampton. On Lawrence’s death, his mother arranged with the Framptons for him to be buried in their family plot at Moreton Church. His coffin was transported on the Frampton estate’s bier. Mourners included Winston and Clementine Churchill and Lawrence’s youngest brother, Arnold.
A bust of Lawrence was placed in the crypt at St Paul’s Cathedral and a stone effigy by Eric Kennington remains in the Anglo-Saxon church of St Martin, Wareham
May 19 2012
Austerity?
Which European leader is serious about economic recovery?
Merkel gives self and ministers pay rise
Merkel, her ministers and their parliamentary secretaries of state will see their wages rise in three stages between now and August 2013, until they all get 5.7 percent more. It is the first pay raise that the German cabinet has taken in twelve years. [..]
She has been the chief advocate of austerity in the eurozone during the debt crisis, earning her criticism from some quarters, notably Greece and more recently France, whose new leader Francois Hollande wants to focus on growth.
As opposed to this:
France Hollande: Ayrault government takes pay cut
France’s new government has held its first cabinet meeting and announced a 30% pay cut for President François Hollande and all his ministers.
A campaign promise, the cut reduces Mr Hollande’s monthly salary from 21,300 euros to 14,910 (£12,000; $19,000).
The cut contrasts sharply with predecessor Nicolas Sarkozy’s decision to increase his pay on entering office.
Austerity?
H/t Chris in Paris @ AMERICAblog
May 18 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Paul Krugman: Apocalypse Fairly Soon
Suddenly, it has become easy to see how the euro – that grand, flawed experiment in monetary union without political union – could come apart at the seams. We’re not talking about a distant prospect, either. Things could fall apart with stunning speed, in a matter of months, not years. And the costs – both economic and, arguably even more important, political – could be huge.
This doesn’t have to happen; the euro (or at least most of it) could still be saved. But this will require that European leaders, especially in Germany and at the European Central Bank, start acting very differently from the way they’ve acted these past few years. They need to stop moralizing and deal with reality; they need to stop temporizing and, for once, get ahead of the curve.
I wish I could say that I was optimistic.
Robert Sheer: Obama Can’t Knock the Hustle
How did we end up with such smart scoundrels? Even after it was known that Jamie Dimon’s bank blew more than $2 billion on the same suspect derivatives trading that has bankrupted the world’s economy, Barack Obama still had praise for the intellect of his political backer and the integrity of the bank he heads: “JPMorgan is one of the best-managed banks there is,” the president told the hosts of ABC’s “The View” in an interview televised Tuesday, adding, “Jamie Dimon, the head of it, is one of the smartest bankers we got. And they still lost $2 billion and counting.”
A lesser bank would have gone under and needed to be bailed out, Obama argued: “That’s why Wall Street reform is so important.” But even when fully implemented, Obama’s tepid reforms would not have stopped this scam and will not stop the others that are sure to follow. Being one of the smartest bankers means you are among those who best know how to skirt the law or, if that cannot be done, how to successfully lobby to gut it.
President Obama doled out the most shocking stream of commencement cliches to the graduating class of Barnard College Monday. To offer just a taste:
“The question is not whether things will get better – they always do… The question is whether together, we can muster the will – in our own lives, in our common institutions, in our politics – to bring about the changes we need. I’m convinced your generation possesses that will.”
Whatever else they possess, the class of 2012 possesses an enormous amount of debt. Heavy borrowing’s not only for graduate students or drop outs from for-profit colleges any more. It’s also for Barnard alums. Forty eight per cent of those graduating this year from Barnard (where the price tag of an education stands at $58,078 ) have taken out loans to pay for their bachelor’s degree. As the New York Times recently pointed out, “Nationally, ninety-four percent of students who earn a bachelor’s degree borrow to pay for higher education – up from 45 percent in 1993.” For these students things aren’t getting better, they’re getting worse. Their will has nothing to do with it.
New York Times Editorial: Germany, the Crisis and the G-8
When the leaders of the Group of 8 gather at Camp David on Friday, President Obama and the others must press Chancellor Angela Merkel of Germany to commit to a euro-zone growth package. This is no time to mince words: Her one-size-fits-all austerity program has been a failure, pushing heavily indebted countries deeper into recession, making it even harder for them to pay off their debts. It is putting the already-weak recovery in the United States at risk and is fueling instability and extremism in Europe.
After months of obstinance, Ms. Merkel has softened her stance – saying that Germany is open to stimulus to spur growth, employment and development in Greece and pledging to work with the new French president, François Hollande, on a program to promote growth across recession-racked Europe. It is unclear, however, whether her comments reflect a true and lasting change of heart.
Richard Reeves: The Tea Is Getting Weaker
LOS ANGELES-Uh-oh! Some people are looking over the right shoulders of the Republicans who rode into the House of Representatives on the tea party wave of 2010. And they don’t like what they’re seeing.
The Club for Growth is fundamentally a conservative lobbying and research group pushing for lower taxes and reduced government spending, which positions itself well to the right of Republican elected officials and even to the right of tea party rhetoric. The club’s basic goal is a flat tax to replace graduated income taxes or a national sales tax. The idea, pardon my liberalism, is to reduce taxation on business and on the rich.
It seems the club has decided that much of the tea party is reneging on its promises of reducing taxes and spending. Last Wednesday it issued a broadside targeting many of the 87 Republican freshmen who roared into the House of Representatives under the rhetorical umbrella of the tea party.
Jenny Dodson: Citizens Fight Back Against Assault on Women’s Health
Not In My Backyard! As Local Government Attacks on Women’s Health Increase, Citizens Are Fighting Back
The vicious attacks on women’s health to which we’ve grown so accustomed on the national and state stages are trickling down to the local level, as municipal and county governments get in on the action. Thankfully, time and again, local citizens have mounted fast and furious responses, resulting in the type of swift and satisfying victories that sometimes feel unimaginable on the national stage.
Local officials around the country have been using the “no taxpayer-funding for abortion” mantra to quietly turn away money for family planning programs that provide vital services for their neediest constituents. These attacks tend to follow a pattern: a program that has been funded without debate for years is suddenly pegged by a politician as “controversial.” Fellow politicians fall in line and vote to defund the program before residents and public health officials have time to react.
But in a few instances, community members are stepping in to stop them once word gets out.
May 18 2012
On This Day In History May 18
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
Click on image to enlarge
May 18 is the 138th day of the year (139th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 227 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1917, U.S. Congress passes Selective Service Act.
Some six weeks after the United States formally entered the First World War, the U.S Congress passes the Selective Service Act on May 18, 1917, giving the U.S. president the power to draft soldiers.
When he went before Congress on April 2, 1917, to deliver his war message, President Woodrow Wilson had pledged all of his nation’s considerable material resources to help the Allies-France, Britain, Russia and Italy-defeat the Central Powers. What the Allies desperately needed, however, were fresh troops to relieve their exhausted men on the battlefields of the Western Front, and these the U.S. was not immediately able to provide. Despite Wilson’s effort to improve military preparedness over the course of 1916, at the time of Congress’s war declaration the U.S. had only a small army of volunteers-some 100,000 men-that was in no way trained or equipped for the kind of fighting that was going on in Europe.
To remedy this situation, Wilson pushed the government to adopt military conscription, which he argued was the most democratic form of enlistment. To that end, Congress passed the Selective Service Act, which Wilson signed into law on May 18, 1917. The act required all men in the U.S. between the ages of 21 and 30 to register for military service. Within a few months, some 10 million men across the country had registered in response to the military draft.
During World War I there were three registrations.
The first, on June 5, 1917, was for all men between the ages of 21 and 31.
The second, on June 5, 1918, registered those who attained age 21 after June 5, 1917. A supplemental registration, included in the second registration, was held on August 24, 1918, for those becoming 21 years old after June 5, 1918.
The third registration was held on September 12, 1918, for men age 18 through 45.
After the signing of the armistice of November 11, 1918, the activities of the Selective Service System were rapidly curtailed. On March 31, 1919, all local, district, and medical advisory boards were closed, and on May 21, 1919, the last state headquarters closed operations. The Provost Marshal General was relieved from duty on July 15, 1919, thereby finally terminating the activities of the Selective Service System of World War I.
May 17 2012
NDAA Detention Provision Ruled Unconstitutional
 In New York City, U.S. District Judge Katherine Forrest ruled that the indefinite detention provision of the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is unconstitutional in violation of the First and Fifth Amendments. The NDAA was signed into law by President Obama in late December after a veto threat over language that was eventually changed at his request.
In New York City, U.S. District Judge Katherine Forrest ruled that the indefinite detention provision of the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) is unconstitutional in violation of the First and Fifth Amendments. The NDAA was signed into law by President Obama in late December after a veto threat over language that was eventually changed at his request.
In a 68-page ruling blocking this statute, U.S. District Judge Katherine Forrest agreed that the statute failed to “pass constitutional muster” because its broad language could be used to quash political dissent.
“There is a strong public interest in protecting rights guaranteed by the First Amendment,” Forrest wrote. “There is also a strong public interest in ensuring that due process rights guaranteed by the Fifth Amendment are protected by ensuring that ordinary citizens are able to understand the scope of conduct that could subject them to indefinite military detention.”
This puts a whole new spin on today’s debate in the House floor Thursday of an amendment to the NDAA proposed by Representatives Adam Smith (D-Wash.) and Justin Amash (R-Mich.), that would undo the detention provisions and bar military detention for any terror suspects captured on U.S. soil. The ruling was made in response to a law suit brought by former New York Times war correspondent and Pulitzer Prize winner, Chris Hedges and others who argued that the law would have a “chilling effect” on their work:
Hedges was joined in the suit by linguist, author and dissident Noam Chomsky, Pentagon whistle-blower Daniel Ellsberg and other high-profile activists, scholars and politicians.
Hedges argued in his testimony that his work as a journalist would bring him into contact with terrorist organizations that would, given the scope of the law, qualify him for indefinite detention. The plaintiffs argued that the threat of detention alone would be an unconstitutional encroachment on their First Amendment rights to free expression and association, as well as a violation of the Fifth Amendment right to due process.
As Glen Greenwald points out in his Salon article, the court rejected the argument by the government that the NDAA did nothing more than the 2001 AUMF already did and thus did not really expand the Government’s power of indefinite detention:
The court cited three reasons why the NDAA clearly expands the Government’s detention power over the 2001 AUMF (all of which I previously cited when denouncing this bill).
First, “by its terms, the AUMF is tied directly and only to those involved in the events of 9/11,” whereas the NDAA “has a non-specific definition of ‘covered person’ that reaches beyond those involved in the 9/11 attacks by its very terms.”
Second, “the individuals or groups at issue in the AUMF are also more specific than those at issue in § 1021″ of the NDAA; that’s because the AUMF covered those “directly involved in the 9/11 attacks while those in § 1021 [of the NDAA] are specific groups and ‘associated forces’.” Moreover, “the Government has not provided a concrete, cognizable set of organizations or individuals that constitute ‘associated forces,’ lending further indefiniteness to § 1021.”
Third, the AUMF is much more specific about how one is guilty of “supporting” the covered Terrorist groups, while the NDAA is incredibly broad and un-specific in that regard, thus leading the court to believe that even legitimate activities could subject a person to indefinite detention.
The court also decisively rejected the argument that President Obama’s signing statement – expressing limits on how he intends to exercise the NDAA’s detention powers – solves any of these problems. That’s because, said the court, the signing statement “does not state that § 1021 of the NDAA will not be applied to otherwise-protected First Amendment speech nor does it give concrete definitions to the vague terms used in the statute.”
(emphasis mine)
A word of caution, we shouldn’t celebrate victory just yet. This is a preliminary injunction issued by one judge and the government will surely appeal it the Circuit Court.
The debate in the House on the amendment to the NDAA introduced by House Armed Services ranking member Adam Smith (D-Wash.) and Rep. Justin Amash (R-Mich.) that would undo the detention provisions and bar military detention for any terror suspects captured on U.S. soil, will go on this afternoon. The amendment has strong bipartisan support in the House. We still need to take action and write our Representatives to vote for this amendment.
May 17 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Robert Reich: The Dog That Didn’t Bark: Obama on JPMorgan
The dog that didn’t bark this week, let alone bite, was the president’s response to JPMorgan Chase’s bombshell admission of losing more than $2 billion in risky derivative trades that should never have been made.
“JPMorgan is one of the best-managed banks there is. Jamie Dimon, the head of it, is one of the smartest bankers we got and they still lost $2 billion,” the president said on the television show The View, which aired Tuesday, suggesting that a weaker bank might not have survived.
That was it.
Not a word about Jamie Dimon’s tireless campaign to eviscerate the Dodd-Frank financial reform bill; his loud and repeated charge that the Street’s near meltdown in 2008 didn’t warrant more financial regulation; his leadership of Wall Street’s brazen lobbying campaign to delay the Volcker Rule under Dodd-Frank, which is still delayed; and his efforts to make that rule meaningless by widening a loophole allowing banks to use commercial deposits to “hedge” (that is, make offsetting bets) their derivative trades.
Jeff Madrick: Germany’s Attempt to Beat Greece Into Submission Won’t Work
Treating Greece like an incorrigible child won’t improve its economy or the future of the eurozone.
“German Patience with Greece Wears Thin,” says the New York Times headline. My patience with the mainstream media also wears thin. Like a bad parent, Germany scolds Greece for something its constant beatings basically forced it to do. The media buys into Germany’s logic. Were high-pressure tactics to adopt punishing austerity cutbacks ever going to encourage Greek solidarity and social peace? Is the parent who beats the child ever going to encourage obedience and healthy behavior? Psychology has taken us a long way past the value of spankings to instill constructive attitudes. It seems not so for the Germans, although it should be said that not all of them agree with their prime minister, Angela Merkel, and government officials.
Are the Germans actually trying to get Greece to leave the euro? If so, they are probably underestimating the turmoil that would cause. On the other hand, it may be getting to the point where it is a better option for the Greeks to incur the possible closing of financial markets should they adopt a new drachma, which will quickly fall in value. They will not pay their debts to German banks and others in full-fledged euros. But they can start to determine their own fate and work with what industries they have. Their export sector is not as weak as people seem to think.
This is the week of the third annual Deficit Fest, the event sponsored by Wall Street billionaire Peter G. Peterson. At this event, many of the people most responsible for the current downturn come together to tell us why we should be worried about the deficit at a time when 25 million people are unemployed, underemployed or have given up looking for work altogether and millions face the prospect of losing their homes.
Past deficit fests included exchanges where Peter Peterson and former Treasury Secretary and Citigroup honcho Robert Rubin mused about their comparative net worth. We also got to witness President Clinton bemoan the fact that the Democratic and Republican leadership in Congress teamed up to prevent him from cutting Social Security. Had Clinton gotten his way, millions of seniors would be getting by on Social Security checks that are more than 10 percent smaller than what they now receive.
Peterson is also known for his sponsorship of the “Economic Sleepwalk” tour, which was officially billed as the “Fiscal Wakeup” tour. This involved sending a group of policy wonks around the country to complain about the budget deficit at a time when the housing bubble was growing to ever more dangerous levels. While some of us were doing our best to warn of the imminent disaster, Peterson was using his money and political connections to dominate media space at a time when the country’s debt-to-GDP ratio was actually falling.
New York Times Editorial: JPMorphing
When he disclosed a stunning $2 billion trading loss at JPMorgan Chase last week, Jamie Dimon, the bank’s chief executive, insisted that the trades had not violated the Volcker Rule, a crucial part of the Dodd-Frank reform law that is supposed to bar banks from doing risky trading for their own account.
This week, however, the story changed. On Monday, a JPMorgan official told The Times that the trades – which have since ballooned to at least $3 billion – started out as allowable, but had “morphed into something” that crossed the line. On Tuesday, at the bank’s annual shareholder meeting, Mr. Dimon echoed that statement, calling for rules to ensure that permitted trades don’t “morph into something different.”
Gail Collins: Fun Plans for Summer Vacation
John Boehner wants to restart the debt-limit debate. This is big news. Remember all the fun we had last time: threats, brinkmanship, wobbling financial markets, torpedoed Grand Bargain? You can certainly understand why he misses it.
The weather’s getting nice. Maybe this time we could do it outdoors.
“Let’s start now!” the House speaker said during a “fiscal summit” in Washington on Tuesday. This is an annual event in which honchos from all political persuasions get together and agree that the national debt is too big.
We are getting into election season, people. We are going to be hearing a lot about the national debt. (Which is very big. Really, at that fiscal summit meeting they were totally in agreement on the bigness.)
E. J. Dionne: Romney’s Clintonesque Moment
Mitt Romney was against Bill Clinton before he was for him.
There was Romney, campaigning Tuesday in Iowa, praising the nation’s last Democratic president and casting him as far superior to the current incumbent.
“Almost a generation ago, Bill Clinton announced that the era of big government was over,” Romney declared. “Clinton was signaling to his own party that Democrats should no longer try to govern by proposing a new program for every problem.” President Obama, he said, “tucked away the Clinton doctrine in his large drawer of discarded ideas.”
So you might assume that Romney likes Clinton. But that would be wrong. Scrambling during the GOP primaries this year to explain why he had voted in the 1992 Massachusetts Democratic presidential primary for the late Sen. Paul Tsongas, Romney invoked that old GOP standby: Clinton hatred.
May 17 2012
On This Day In History May 17
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
Click on image to enlarge
May 17 is the 137th day of the year (138th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 228 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1954, in a major civil rights victory, the U.S. Supreme Court hands down an unanimous decision in Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, ruling that racial segregation in public educational facilities is unconstitutional. The historic decision, which brought an end to federal tolerance of racial segregation, specifically dealt with Linda Brown, a young African American girl who had been denied admission to her local elementary school in Topeka, Kansas, because of the color of her skin.
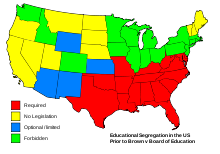
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. The decision overturned the Plessy v. Ferguson decision of 1896 which allowed state-sponsored segregation. Handed down on May 17, 1954, the Warren Court’s unanimous (9-0) decision stated that “separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.” As a result, de jure racial segregation was ruled a violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment of the United States Constitution. This ruling paved the way for integration and the civil rights movement.
The case of Brown v. Board of Education as heard before the Supreme Court combined five cases: Brown itself, Briggs v. Elliott (filed in South Carolina), Davis v. County School Board of Prince Edward County (filed in Virginia), Gebhart v. Belton (filed in Delaware), and Bolling v. Sharpe (filed in Washington D.C.).
All were NAACP-sponsored cases. The Davis case, the only case of the five originating from a student protest, began when sixteen-year-old Barbara Rose Johns organized and led a 450-student walkout of Moton High School.
The Kansas case was unique among the group in that there was no contention of gross inferiority of the segregated schools’ physical plant, curriculum, or staff. The district court found substantial equality as to all such factors. The Delaware case was unique in that the District Court judge in Gebhart ordered that the black students be admitted to the white high school due to the substantial harm of segregation and the differences that made the schools separate but not equal. The NAACP’s chief counsel, Thurgood Marshall, who was later appointed to the U.S. Supreme Court in 1967, argued the case before the Supreme Court for the plaintiffs. Assistant attorney general Paul Wilson, later distinguished emeritus professor of law at the University of Kansas, conducted the state’s ambivalent defense in his first appellate trial.
Unanimous Opinion and Key Holding
In spring 1953 the Court heard the case but was unable to decide the issue and asked to rehear the case in fall 1953, with special attention to whether the Fourteenth Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause prohibited the operation of separate public schools for whites and blacks.
The case was being reargued at the behest of Associate Justice Felix Frankfurter, who used re-argument as a stalling tactic, to allow the Court to gather a unanimous consensus around a Brown opinion that would outlaw segregation. Chief Justice Vinson had been a key stumbling block. The justices in support of desegregation spent much effort convincing those who initially dissented to join a unanimous opinion. Even though the legal effect would be same for a majority versus unanimous decision, it was felt that it was vital to not have a dissent which could be relied upon by opponents of desegregation as a legitimizing counterargument.
Conference notes and draft decisions illustrate the division of opinions before the decision was issued. Justices Douglas, Black, Burton, and Minton were predisposed to overturn Plessy. Fred M. Vinson noted that Congress had not issued desegregation legislation; Stanley F. Reed discussed incomplete cultural assimilation and states’ rights and was inclined to the view that segregation worked to the benefit of the African-American community; Tom C. Clark wrote that “we had led the states on to think segregation is OK and we should let them work it out.” Felix Frankfurter and Robert H. Jackson disapproved of segregation, but were also opposed to judicial activism and expressed concerns about the proposed decision’s enforceability. After Vinson died in September 1953, President Dwight D. Eisenhower appointed Earl Warren as Chief Justice. Warren had supported the integration of Mexican-American students in California school systems following Mendez v. Westminster.
While all but one justice personally rejected segregation, the self-restraint faction questioned whether the Constitution gave the Court the power to order its end. The activist faction believed the Fourteenth Amendment did give the necessary authority and were pushing to go ahead. Warren, who held only a recess appointment, held his tongue until the Senate, dominated by southerners, confirmed his appointment.
Warren convened a meeting of the justices, and presented to them the simple argument that the only reason to sustain segregation was an honest belief in the inferiority of Negroes. Warren further submitted that the Court must overrule Plessy to maintain its legitimacy as an institution of liberty, and it must do so unanimously to avoid massive Southern resistance. He began to build a unanimous opinion.
Although most justices were immediately convinced, Warren spent some time after this famous speech convincing everyone to sign onto the opinion. Justices Robert Jackson and Stanley Reed finally decided to drop their dissent to what was by then an opinion backed by all the others. The final decision was unanimous. Warren drafted the basic opinion and kept circulating and revising it until he had an opinion endorsed by all the members of the Court.
The key holding of the Court was that, even if segregated black and white schools were of equal quality in facilities and teachers, segregation by itself was harmful to black students and unconstitutional. They found that a significant psychological and social disadvantage was given to black children from the nature of segregation itself, drawing on research conducted by Kenneth Clark assisted by June Shagaloff. This aspect was vital because the question was not whether the schools were “equal”, which under Plessy they nominally should have been, but whether the doctrine of separate was constitutional. The justices answered with a strong “no”:
Does segregation of children in public schools solely on the basis of race, even though the physical facilities and other “tangible” factors may be equal, deprive the children of the minority group of equal educational opportunities? We believe that it does… Segregation of white and colored children in public schools has a detrimental effect upon the colored children. The impact is greater when it has the sanction of the law, for the policy of separating the races is usually interpreted as denoting the inferiority of the negro group. A sense of inferiority affects the motivation of a child to learn. Segregation with the sanction of law, therefore, has a tendency to [retard] the educational and mental development of negro children and to deprive them of some of the benefits they would receive in a racial[ly] integrated school system… We conclude that, in the field of public education, the doctrine of “separate but equal” has no place. Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal. Therefore, we hold that the plaintiffs and others similarly situated for whom the actions have been brought are, by reason of the segregation complained of, deprived of the equal protection of the laws guaranteed by the Fourteenth Amendment.
May 16 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Wednesday is Ladies’ Day
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
Katrina vanden Heuvel: It’s time to break up the big banks
Consider $2 billion lost on a bad bet, plus billions more as investors dumped the stock, a providential warning. When Jamie Dimon, the imperious head of JPMorgan Chase, revealed that the bank had lost so much on a derivatives trade gone bad, it was clear warning that, four years after blowing up the economy, the big banks are still playing with bombs. [..]
When Dimon testified before the Financial Crisis Inquiry Commission in 2010, he said that when his daughter asked him what a financial crisis was, he told her “it’s something that happens every five to seven years.” He seems intent on validating his prediction.
But the United States went for decades without a financial crisis after the New Deal regulations shackled the banks. It was only with deregulation under Reagan and Clinton that financial crises have been inflicted on us regularly. Now Dimon’s bank’s bad bets have given us one last warning: It is time to break up the big banks
Maira Sutton: Internet Freedom Activists Protest Secret Trade Agreement Being Negotiated This Week
The U.S. content industry will try anything to preserve its profit margin and power over the creative content market at the expense of the Internet. They will use any tactic that circumvents democratic processes to make new rules for the Internet that favor their interests and not the interests of Internet users or the technical community that actually builds the Internet as we know it. The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) is yet another example of these tactics.
The TPP is a secretive plurilateral1 agreement that includes provisions dealing with intellectual property, including online copyright enforcement, anti-circumvention measures, and Internet intermediary liability. Due to the secrecy of the negotiations, we do not know what is in the current version of the TPP’s IP chapter; the general public has only seen a leaked February 2011 version of the U.S. IP chapter proposal pdf. Based on the one-sided nature of the groups directly involved, and the content of what has already leaked, we should all be concerned about the prospect of the TPP including provisions that will harm online expression, privacy and innovation on the Internet.
J.P. Morgan’s CEO Jamie Dimon once sarcastically complained that all his traders would need to talk to a psychiatrist in order to comply with regulations. Now, in the absence of strict regulations, every trader on the street is psychoanalyzing Dimon’s every word in order to try to make money off J.P. Morgan’s very large mistake.
Back in February, Dimon famously told Fox Business that because of the Volcker Rule for “every trader, we are going to have to have a lawyer, a compliance officer, a doctor to see what their testosterone levels are, and a shrink, ‘what is your intent?’ ” But now it is J.P. Morgan’s intent in a $100 billion bet that has sent the financial media abuzz with questions. The $2 billion loss that J.P. Morgan has incurred related to this position has only further fueled the speculations about what, exactly, J.P. Morgan was trying to do with this trade.
Robin Wells: German voters must break the Merkel mindset that got them into this
Greece’s euro membership was as much the German elite’s fault as anyone’s. Can it find the leadership to resolve the crisis?
Sunday’s regional German elections offer a small ray of hope. Merkel’s party received a thrashing in North Rhine-Westphalia, home to nearly one in five Germans. Rejecting the conservatives’ hard-line platform of more austerity and finger-pointing, German voters instead voted for the Social Democrats, for a platform of more spending and, shockingly, for more debt. This caps a series of defeats in state elections for Merkel and makes it increasingly clear that her government is in serious jeopardy.
Perhaps, just perhaps, German voters are waking up. And therein lies the possibility that the euro can be saved.
But it’s a race against time at this point. Precious time, credibility and resources have been lost. Lives have been up-ended and shattered, voters are angry and restive, markets are in a hostile and unforgiving mood. It is said that leaders are born of great crises. It is now or never for Germany.
Jessica Valenti: Year of the (Young) Woman
Komen. Sandra Fluke. Transvaginal. The reason these words are instantly recognizable-the reason the “war on women” is now part of the national conversation-is largely thanks to younger women and online organizing. Behind every recent battle against the onslaught of sexism has been the energy and activism of young people-on blogs, Twitter, Tumblr and Faebook. And in a long-overdue but welcome change of message, the mainstream feminist movement that once claimed young women didn’t care about feminism is finally catching on. Some are even walking the walk.
Last week, NARAL Pro-Choice America President Nancy Keenan announced that she would be stepping down from her role to make way for younger activists. She told Sarah Kliff at the Washington Post, “There’s an opportunity for a new and younger leader.”
“People give a lot of lip service to how we’re going to engage the next generation, but we can’t just assume it will happen on its own.”
Sarah Anderson: Nurses Push Tax on Trades to Help Sick
Of all the street actions leading up to the NATO summit, the one that might seem most perplexing is a nurses’ rally for a tax on securities trades. Financial markets are pretty remote from hospital bedsides, you might think.
Why would nurses get mixed up in an issue like that?
RoseAnn DeMoro, executive director of National Nurses United, says there’s a simple explanation: “The big banks, investment firms and other financial institutions, which ruined the economy with trillion-dollar trades on people’s homes and pensions and similar reckless gambling, should pay for the recovery.”
Nurses have been on the front lines of the crisis, seeing firsthand the health impacts of skyrocketing poverty and record high rates of uninsured Americans.
May 16 2012
On This Day In History May 16
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
Click on image to enlarge
May 16 is the 136th day of the year (137th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 229 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1868, the U.S. Senate votes against impeaching President Andrew Johnson and acquits him of committing “high crimes and misdemeanors.”
In February 1868, the House of Representatives charged Johnson with 11 articles of impeachment for vague “high crimes and misdemeanors.” (For comparison, in 1998, President Bill Clinton was charged with two articles of impeachment for obstruction of justice during an investigation into his inappropriate sexual behavior in the White House Oval Office. In 1974, Nixon faced three charges for his involvement in the Watergate scandal.) The main issue in Johnson’s trial was his staunch resistance to implementing Congress’ Civil War Reconstruction policies. The War Department was the federal agency responsible for carrying out Reconstruction programs in the war-ravaged southern states and when Johnson fired the agency’s head, Edwin Stanton, Congress retaliated with calls for his impeachment.
Of the 11 counts, several went to the core of the conflict between Johnson and Congress. The House charged Johnson with illegally removing the secretary of war from office and for violating several Reconstruction Acts. The House also accused the president of hurling slanderous “inflammatory and scandalous harangues” against Congressional members. On February 24, the House passed all 11 articles of impeachment and the process moved into a Senate trial.
May 16 2012
Why the $2 Billion Chase Loss Matters to Everyone
Felix Salmon, finance blogger at Reuters and Matt Taibbi, of ‘vampire squid” fame from “Rolling Stone“, were guests on “View Point with Eliot Spitzer“, discussing the implications JPMorgan’s $2 billion trading loss and why it should matter to anyone with a banking account at Chase, or any other to big to fail bank.
Taibbi and Salmon agree JPMorgan’s risk-taking has broad implications. “JPMorgan Chase takes deposits in from every single mom and pop, and small business and large business, in the world, and the President of the United States,” Salmon says. “They’re a utility bank and it is their job and their duty … to take those deposits and lend them out into the economy. And what do they do instead? They take $360 billion and put it in a hedge fund in London.”
Jamie Dimon’s failure
by Felix Salmon
Drew’s Chief Investment Office quadrupled in size between 2006 and 2011, reaching $356 billion in total, and it’s easy to see how that happened. On the one hand, it was incredibly profitable, with the London team alone, which oversaw some $200 billion, making $5 billion of profit in 2010, more than 25% of JP Morgan’s net income for the year. At the same time JP Morgan accumulated enormous new deposits in the wake of the financial crisis, both by acquiring banks and by attracting big new clients wanting the safety of a too-big-to-fail bank. Historically, JP Morgan has served big corporations by lending them money, but nowadays, as the cash balances on corporate balance sheets get ever more enormous, the main thing these companies want from JP Morgan is a simple checking account – one where they can be sure that their money is safe.
With lots of deposits coming in, and little corporate demand for loans, it was easy for all that money to find its way to the Chief Investment Office, which could take any amount of liabilities (deposits are liabilities, for a bank) and turn them into assets generating billions of dollars in profits.
Never mind the weak tea Volker rule, what is needed is a new, revised Glass-Steagal, the break up the TBTF and protection for investors and the economy.


Recent Comments