Author's posts
Jan 19 2012
On this Day In History January 19
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
January 19 is the 19th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar. There are 346 days remaining until the end of the year (347 in leap years).
On this day in 1853, Giuseppe Verdi‘s opera Il Trovatore receives its premiere performance in Rome.
Il trovatore (The Troubadour) is an opera in four acts by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Salvadore Cammarano, based on the play El Trovador (1836) by Antonio Garcia Gutierrez. Cammarano died in mid-1852 before completing the libretto. This gave the composer the opportunity to propose significant revisions, which were accomplished under his direction by the young librettist, Leone Emanuele Bardare, and they are seen largely in the expansion of the role of Leonora.
The opera was first performed at the Teatro Apollo, Rome, on 19 January 1853 where it “began a victorious march throughout the operatic world”. Today it is given very frequently and is a staple of the standard operatic repertoire. It appears at number 17 on Opera America‘s list of the 20 most-performed operas in North America.
Enrico Caruso once said that all it takes for successful performance of Il trovatore is the four greatest singers in the world. On many different occasions, this opera and its music have been featured in various forms of popular culture and entertainment. Scenes of comic chaos play out over a performance of Il trovatore in the Marx Brothers‘s film, A Night at the Opera. Luchino Visconti used a performance of Il trovatore at La Fenice opera house for the opening sequence of his 1954 film Senso. As Manrico sings his battle cry in “Di quella pira”, the performance is interrupted by the answering cries of Italian nationalists in the audience. In Italian Film in the Light of Neorealism, Millicent Marcus proposes that Visconti used this operatic paradigm throughout Senso, with parallels between the opera’s protagonists, Manrico and Leonora, and the film’s protagonists, Ussoni and Livia.
Jan 19 2012
Both SOPA And PIPA Stopped For Now
 It certainly been an eventful day. The two bills, Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and Protect Intellectual Property Act (PIPA), were defeated Wednesday by an internet blackout of key web sites and the avalanche of petitions, street protests, e-mails and phone calls to congressional members.
It certainly been an eventful day. The two bills, Stop Online Piracy Act (SOPA) and Protect Intellectual Property Act (PIPA), were defeated Wednesday by an internet blackout of key web sites and the avalanche of petitions, street protests, e-mails and phone calls to congressional members.
When the powerful world of old media mobilized to win passage of an online antipiracy bill, it marshaled the reliable giants of K Street – the United States Chamber of Commerce, the Recording Industry Association of America and, of course, the motion picture lobby, with its new chairman, former Senator Christopher J. Dodd, the Connecticut Democrat and an insider’s insider.
Yet on Wednesday this formidable old guard was forced to make way for the new as Web powerhouses backed by Internet activists rallied opposition to the legislation through Internet blackouts and cascading criticism, sending an unmistakable message to lawmakers grappling with new media issues: Don’t mess with the Internet. [..]
Congress now follows Bank of America, Verizon and Netflix as the latest institution to be forced to change course by an internet led revolt.
It was especially dismaying that First Amendment stalwarts, like Senator Patrick Leahy and Representative John Conyers Jr. of Michigan, were sponsoring this bill. It took Republicans in the House, assisted by Paul Ryan (R-WI) and, initially, six Republican senators to get both bill pulled from consideration. To his credit, Sen. Ron Wyden (D-OR) was a one man road block to PIPA until the Republicans, pressured by their House compatriots, pulled their support.
So, besides Sen. Wyden, why weren’t there more Democrats opposed? Why were they even supporting a bill that would infringe on free speech and hurt job growth in the technology field? Follow the money. Hollywood, the music and movie industry, are a big supporters of anti-piracy and IP protection laws and Democrats.
Former Senator, Chris Dodd (D-CT), who forswore a lobbying career but is now CEO of Motion Picture Assn. of America, railed against technology companies such as Google, Mozilla and Wikipedia calling the blackout a “stunt”:
“It is an irresponsible response and a disservice to people who rely on them for information and who use their services,” Dodd said in a statement. “It is also an abuse of power given the freedoms these companies enjoy in the marketplace today.”
It wasn’t until Saturday that President Obama spoke out about the most controversial portions of the House bill that would require Internet service providers to block infringing websites but said nothing about PIPA, the Senate version, and fell short of saying he would veto the bill.
Up until the last few days the media, especially television and cable have been pretty silent. Chris Hayes of MSNBC’s “Up with Chris” hosted a debate with NBC Universal’s General Counsel, Richard Cotton, Alexis Ohanian, co-founder of Reddit.com, former Rep. Joe Sestak (D-PA) and former lobbyist Jack Abramoff. Since it became apparent that the traditional media was missing the boat on one of the biggest news stories of the year, they all started jumping back on the ship.
Wednesday night, Mr. Hayes was a guest on “The Rachel Maddow Show” where he and Rachel talked about the power and effectiveness of the online protest in influencing Congress who by and large didn’t understand the bills or the internet.
Will this stop these two bills? No, it won’t. As Wikipedia points out in its thank you to its visitors, “we’re not done yet”
SOPA sponsor Lamar Smith stated that the House of Representatives will push the bill forward in February. Senate sponsor Patrick Leahy still plans for a PIPA vote on January 24.
Moreover, SOPA and PIPA are symptoms of a larger issue. They are misguided solutions to a misunderstood problem. In the U.S. and abroad, legislators and big media are embracing censorship and sacrificing civil liberties in their attacks on free knowledge and an open Internet.
Although support has slipped in both the Senate and the House, there is a Senate vote on PIPA scheduled for January 24, and the House will be moving forward as well. It is important to keep the pressure up on both houses. We expect changes that appear to tone down the damaging effects of the laws, without addressing their fundamental flaws.
Keep calling your representatives! Tell them you believe in a free and open Internet!
It looks like this is just start of the war to save the internet.
Jan 18 2012
On this Day In History January 18
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
January 18 is the 18th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar. There are 347 days remaining until the end of the year (348 in leap years).
On this day in 1865, the United States House of Representatives passes the 13th Amendment to the Constitution, abolishing slavery in the United States. It read, “Neither slavery nor involuntary servitude…shall exist within the United States, or any place subject to their jurisdiction.”
The Thirteenth Amendment to the United States Constitution officially abolished and continues to prohibit slavery and involuntary servitude, except as punishment for a crime. It was passed by the Senate on April 8, 1864, passed by the House on January 31, 1865, and adopted on December 6, 1865. On December 18, Secretary of State William H. Seward, in a proclamation, declared it to have been adopted. It was the first of the Reconstruction Amendments.
President Lincoln was concerned that the Emancipation Proclamation, which outlawed slavery in the ten Confederate states still in rebellion in 1863, would be seen as a temporary war measure, since it was based on his war powers and did not abolish slavery in the border states.
The first twelve amendments were adopted within fifteen years of the Constitution’s adoption. The first ten (the Bill of Rights) were adopted in 1791, the Eleventh Amendment in 1795 and the Twelfth Amendment in 1804. When the Thirteenth Amendment was proposed there had been no new amendments adopted in more than sixty years.
During the secession crisis, but prior to the outbreak of the Civil War, the majority of slavery-related bills had protected slavery. The United States had ceased slave importation and intervened militarily against the Atlantic slave trade, but had made few proposals to abolish domestic slavery, and only a small number to abolish the domestic slave trade. Representative John Quincy Adams had made a proposal in 1839, but there were no new proposals until December 14, 1863, when a bill to support an amendment to abolish slavery throughout the entire United States was introduced by Representative James Mitchell Ashley (Republican, Ohio). This was soon followed by a similar proposal made by Representative James F. Wilson(Republican, Iowa).
Eventually the Congress and the public began to take notice and a number of additional legislative proposals were brought forward. On January 11, 1864, Senator John B. Henderson of Missouri submitted a joint resolution for a constitutional amendment abolishing slavery. The abolition of slavery had historically been associated with Republicans, but Henderson was one of the War Democrats. The Senate Judiciary Committee, chaired by Lyman Trumbull (Republican, Illinois), became involved in merging different proposals for an amendment. On February 8 of that year, another Republican, Senator Charles Sumner (Radical Republican, Massachusetts), submitted a constitutional amendment to abolish slavery as well as guarantee equality. As the number of proposals and the extent of their scope began to grow, the Senate Judiciary Committee presented the Senate with an amendment proposal combining the drafts of Ashley, Wilson and Henderson.
Originally the amendment was co-authored and sponsored by Representatives James Mitchell Ashley (Republican, Ohio) and James F. Wilson (Republican, Iowa) and Senator John B. Henderson (Democrat, Missouri).
While the Senate did pass the amendment on April 8, 1864, by a vote of 38 to 6, the House declined to do so. After it was reintroduced by Representative James Mitchell Ashley, President Lincoln took an active role in working for its passage through the House by ensuring the amendment was added to the Republican Party platform for the upcoming Presidential elections. His efforts came to fruition when the House passed the bill on January 31, 1865, by a vote of 119 to 56. The Thirteenth Amendment’s archival copy bears an apparent Presidential signature, under the usual ones of the Speaker of the House and the President of the Senate, after the words “Approved February 1, 1865”.
The Thirteenth Amendment completed the abolition of slavery, which had begun with the Emancipation Proclamation issued by President Abraham Lincoln in 1863.
Shortly after the amendment’s adoption, selective enforcement of certain laws, such as laws against vagrancy, allowed blacks to continue to be subjected to involuntary servitude in some cases.
The Thirteenth Amendment was followed by the Fourteenth Amendment (civil rights in the states), in 1868, and the Fifteenth Amendment (which bans racial voting restrictions), in 1870.
Jan 17 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Robert Reich: Free Enterprise on Trial
Mitt Romney is casting the 2012 campaign as “free enterprise on trial” – defining free enterprise as achieving success through “hard work and risking-taking.” Tea-Party favorite Senator Jim DeMint of South Carolina says he’s supporting Romney because “we really need someone who understands how risk, taking risk … is the way we create jobs, create choices, expand freedom.” Chamber of Commerce President Tom Donahue, defending Romney, explains “this economy is about risk. If you don’t take risk, you can’t have success.”
Wait a minute. Who do they think are bearing the risks? Their blather about free enterprise risk-taking has it upside down. The higher you go in the economy, the easier it is to make money without taking any personal financial risk at all. The lower you go, the bigger the risks.
Bill McKibben: Agitators in the Oilsands Debates are Working for Oil Companies
I’ve been visiting Canada all my life, but I’m a little worried about my upcoming trip.
In late March I’m supposed to come to Vancouver to give a couple of talks. Youth Action Canada invited me to come, to speak to college students from across the country; I’m also planning to do a benefit for the Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives. But now I read that Joe Oliver, the country’s natural resources minister, is condemning “environmental and other radical groups that would seek to block” the Northern Gateway pipeline from the oilsands of Alberta to the Pacific.
I think he’s talking about people like me. I’ve spent much of the last year helping rally opposition to the Key-stone XL pipeline from the oilsands to the Gulf of Mexico. I was arrested outside the White House in August, and emceed the demonstration that brought thousands of people to circle the White House in November. When I come to British Columbia, I’ll urge everyone I meet to oppose the Gate-way project. In fact, Youth Action is paying me to come. And the money will end up at 350.org, the international climate change campaign, helping fight projects like Gateway around the world.
From all evidence, the issue of economic justice isn’t going away. Break the news gently to Mitt Romney, who seems apoplectic that the whole “rich get richer, poor get poorer” thing is being discussed out loud. In front of the children, for goodness’ sake.
“You know I think it’s fine to talk about those things in quiet rooms,” he told the “Today” show’s Matt Lauer last week. “But the president has made this part of his campaign rally. Everywhere he goes we hear him talking about millionaires and billionaires and executives and Wall Street. It’s a very envy-oriented, attack-oriented approach.”
Actually, those blasts weren’t comimg from President Obama. That was Romney’s competition for the Republican nomination, sounding like a speakers’ lineup at an Occupy Wall Street rally.
Charles M. Blow: Newt Gingrich and the Art of Racial Politics
I’ll spare you the video. TMC
That’s the way I like to spend my Martin Luther King, Jr. Day: watching Newt Gingrich sneer at Juan Williams, a black man, for having the temerity to ask him if his condescending remarks about the work ethic of poor black people are indeed condescending:
Juan Williams: Speaker Gingrich, you recently said black Americans should demand jobs, not food stamps. You also say poor kids lack a strong work ethic and proposed having them work as janitors in their schools. Can’t you see that this is viewed as at a minimum as insulting to all Americans but particularly to black Americans?
Newt Gingrich: No, I don’t see that (applause).
Gingrich went on to say that the children would be “getting money, which is a good thing if you’re poor. Only the elites despise earning money.”
The first implication here is that elites are liberals, not men like Gingrich – whose net worth The Los Angeles Times has estimated to be $6.7 million, who was a history professor, who was paid $1.6 million dollars by Freddie Mac for “advice,” and who had a half million dollar line of credit at Tiffany’s.
If Gingrich isn’t among America’s elite, the word no longer has meaning.
New York Times Editorial: Taxes and Transparency
Barack Obama released his tax records when he ran for president in 2008. So did Richard Nixon in 1968. In fact, so did George Romney in that same campaign.
But, in 2012, Mitt Romney, the former governor of Massachusetts and onetime chief executive of a private equity firm, is still hedging about whether he will do so.
Candidates for the presidency are not legally required to release their tax records, but they generally have for many years now – because American voters have a right to know how the men and women who want to be president make their money.
Barry Lando: Iran, the U.S. and Israel: Blind Man’s Bluff
In a perilous spiral of assassinations, threats and counterthreats, leaders in Washington, Jerusalem and Tehran keep ratcheting up the tension. What is most alarming about the situation is that the principal players and their advisers are engaged in an incredibly dangerous three-way game of blind man’s bluff.
None of them expresses a real understanding of the others-their motives, their concerns or their likely reactions. That’s true even for Israel and the United States: Though the U.S. risks being sucked into any conflict between Israel and Iran, the Obama administration is currently forced to guess what its supposed allies in Israel are planning.
Jan 17 2012
Protesting SOPA, Web Sites Go Dark
 Over the weekend the discussion about bills pending in Congress that would change the Internet has started to get some attention. Opposition to Stop Internet Piracy Act, House version and the Senate’s version, Protect the Internet Privacy Act came from the White House in a statement expressing concerns that the bills would stifle innovation and infringe on free speech and lead to “online censorship of lawful activity.” While the White House statement did not say Pres. Obama would veto it, it was a clear condemnation of the flaws critics have pointed to in the bill.
Over the weekend the discussion about bills pending in Congress that would change the Internet has started to get some attention. Opposition to Stop Internet Piracy Act, House version and the Senate’s version, Protect the Internet Privacy Act came from the White House in a statement expressing concerns that the bills would stifle innovation and infringe on free speech and lead to “online censorship of lawful activity.” While the White House statement did not say Pres. Obama would veto it, it was a clear condemnation of the flaws critics have pointed to in the bill.
One of the most controversial portions of the House bill that would require Internet service providers to block infringing websites was removed completely by House Judiciary Chairman Lamar Smith (R-TX). Rep. Darrel Issa (R-CA) secured a promise from Majority Leader Eric Cantor (R-VA) that the House will not vote unless there is consensus on the bill. A Reddit campaign managed to persuade Rep. Paul Ryan (R-WI) to oppose the bill, for instance.
On the Senate side, PIPA had up unit now blocked by a lone senator, Ron Wyden (D-OR. He has now been joined by Sen. Ben Cardin (D-MD)and Mark Udall (D-CO). Similarly, six Republican Senators, including two co-sponsors — Senators Orrin Hatch (R-UT), Chuck Grassley (R-IA) (the two co-sponsors) along with John Cornyn (R-TX), Jeff Sessions (R-AL), Mike Lee (R-UT) and Tom Coburn (R-OK) — have asked Aenate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D_NV)not to bring the cloture vote he’s promised to bring on the 24th. Sen. Pat Leahy, a key sponsor of the Protect IP Act, has conceded that more study is needed for the provisions that would allow rogue sites to be delisted from the Domain Name Service (basically the Internet’s phone directory). Critics have warned that mucking with DNS could splinter the architecture of the Internet.
On Wednesday beginning at midnight, several major web sites will go dark for 24 hours. Websites Wikpedia, Reddit, Craig’s List and ICanHasCheezburger.com are among the larger sites that will participate. The document-sharing site Scribd, for instance, made a billion pages vanish to protest the bill. Wikipedia users can view proposed designs for “blackout pages,” which may appear in place of normal Wikipedia entries during the protest on January 18.
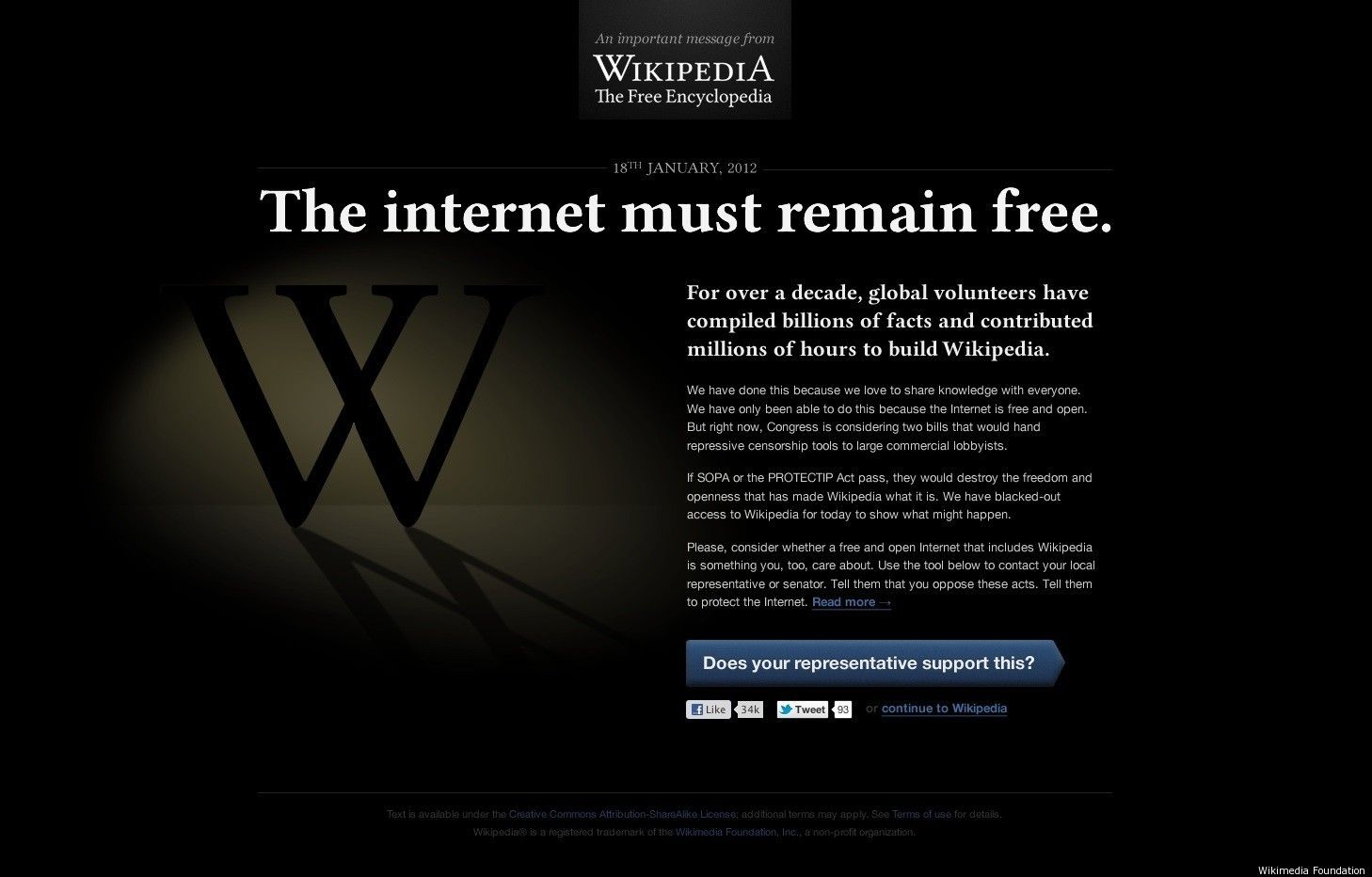
click on image to enlarge.
In New York City, New York Tech Meetup, a 20,000 member community of people working in the New York Tech Industry are protesting the pending legislation in from of the offices of Senators Charles Schumer and Kirsten Gillibrand who are still supporting the bill and urging Sen. Reid to bring the bill to the floor for cloture. One of the largest areas of job growth in NYC has been in the tech industries. New York Tech believes that SOPA, besides threatening freedom of speech, will kill those jobs.
You can physically join the NYC Protest at this site:
When: Wednesday January 18, 2012
Time 12:30-2:00PM
Where: 780 Third Ave (at 49th street) – outside the offices of New York Senators Charles Schumer and Kirsten Gillibrand
Jan 17 2012
On this Day In History January 17
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
January 17 is the 17th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar. There are 348 days remaining until the end of the year (349 in leap years).
On this day in 1961, President Dwight D. Eisenhower delivers his farewell address to the nation warning the American people to keep a careful eye on what he calls the “military-industrial complex” that has developed in the post-World War II years.
A fiscal conservative, Eisenhower had been concerned about the growing size and cost of the American defense establishment since he became president in 1953. In his last presidential address to the American people, he expressed those concerns in terms that frankly shocked some of his listeners.
Eisenhower began by describing the changing nature of the American defense establishment since World War II. No longer could the U.S. afford the “emergency improvisation” that characterized its preparations for war against Germany and Japan. Instead, the United States was “compelled to create a permanent armaments industry” and a huge military force. He admitted that the Cold War made clear the “imperative need for this development,” but he was gravely concerned about “the acquisition of unwarranted influence…by the military-industrial complex.” In particular, he asked the American people to guard against the “danger that public policy could itself become the captive of a scientific-technological elite.”
Military-industrial complex (MIC) is a concept commonly used to refer to policy relationships between governments, national armed forces, and the industrial sector that supports them. These relationships include political approval for research, development, production, use, and support for military training, weapons, equipment, and facilities within the national defense and security policy. It is a type of iron triangle.
The term is most often played in reference to the military of the United States, where it gained popularity after its use in the farewell address speech of President Dwight D. Eisenhower, though the term is applicable to any country with a similarly developed infrastructure.
It is sometimes used more broadly to include the entire network of contracts and flows of money and resources among individuals as well as institutions of the defense contractors, The Pentagon, and the Congress and executive branch. This sector is intrinsically prone to principal-agent problem, moral hazard, and rent seeking. Cases of political corruption have also surfaced with regularity.
A similar thesis was originally expressed by Daniel Guerin, in his 1936 book Fascism and Big Business, about the fascist government support to heavy industry. It can be defined as, “an informal and changing coalition of groups with vested psychological, moral, and material interests in the continuous development and maintenance of high levels of weaponry, in preservation of colonial markets and in military-strategic conceptions of internal affairs”.
Jan 16 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Jonathan Turley: 10 reasons the U.S. is no longer the land of the free
Every year, the State Department issues reports on individual rights in other countries, monitoring the passage of restrictive laws and regulations around the world. Iran, for example, has been criticized for denying fair public trials and limiting privacy, while Russia has been taken to task for undermining due process. Other countries have been condemned for the use of secret evidence and torture.
Even as we pass judgment on countries we consider unfree, Americans remain confident that any definition of a free nation must include their own – the land of free. Yet, the laws and practices of the land should shake that confidence. In the decade since Sept. 11, 2001, this country has comprehensively reduced civil liberties in the name of an expanded security state. The most recent example of this was the National Defense Authorization Act, signed Dec. 31, which allows for the indefinite detention of citizens. At what point does the reduction of individual rights in our country change how we define ourselves?
Paul Krugman: How Fares the Dream?
“I have a dream,” declared Martin Luther King, in a speech that has lost none of its power to inspire. And some of that dream has come true. When King spoke in the summer of 1963, America was a nation that denied basic rights to millions of its citizens, simply because their skin was the wrong color. Today racism is no longer embedded in law. And while it has by no means been banished from the hearts of men, its grip is far weaker than once it was.
To say the obvious: to look at a photo of President Obama with his cabinet is to see a degree of racial openness – and openness to women, too – that would have seemed almost inconceivable in 1963. When we observe Martin Luther King’s Birthday, we have something very real to celebrate: the civil rights movement was one of America’s finest hours, and it made us a nation truer to its own ideals.
The year 2011 will be remembered as the time when many ever-optimistic Americans began to give up hope. President John F. Kennedy once said that a rising tide lifts all boats. But now, in the receding tide, Americans are beginning to see not only that those with taller masts had been lifted far higher, but also that many of the smaller boats had been dashed to pieces in their wake.
In that brief moment when the rising tide was indeed rising, millions of people believed that they might have a fair chance of realizing the “American Dream.” Now those dreams, too, are receding. By 2011, the savings of those who had lost their jobs in 2008 or 2009 had been spent. Unemployment checks had run out. Headlines announcing new hiring – still not enough to keep pace with the number of those who would normally have entered the labor force – meant little to the 50 year olds with little hope of ever holding a job again.
New York Times Editorial: On the Trail of Mortgage Fraud
President Obama should form a task force to investigate and pursue potential civil and criminal wrongdoing by institutions and people whose conduct had the greatest economic impact.
Queens has been harder hit by foreclosures than any other New York borough, and the Federal Bureau of Investigation believes it has found a culprit. Last July, the F.B.I. accused Edul Ahmad, a local broker, of a $50 million mortgage fraud, saying he lured fellow immigrants into subprime mortgages, inflated the values of their properties and concealed his involvement in deals that were ruinous for scores, if not hundreds, of borrowers. Mr. Ahmad pleaded not guilty, and posted $2.5 million bail. Now, according to court papers, as reported in The Times, he is plea-bargaining with federal prosecutors.
Whatever Mr. Ahmad did or did not do, one thing is sure: he did not act alone. The attention Mr. Ahmad has drawn highlights the relative lack of scrutiny of the big banks and their senior executives. Big banks created demand and provided credit for dubious mortgage loans, which they bundled into securities and sold to investors. If not for reckless lending and heedless securitizing, there would have been no mortgage bubble and no mortgage bust – and, in all probability, no Edul Ahmad.
Eugene Robinson: The Dream That Came True
He would be an elder statesman now, a lion in winter, an American hero perhaps impatient with the fuss being made over his birthday. At 83, he’d likely still have his wits and his voice. Surely, if he were able, he would continue to preach, and to pray-and to dream.
For the Rev. Martin Luther King Jr., dreaming was not optional. It was a requirement of citizenship to envision a fairer, more prosperous nation no longer shackled by racism and poverty. It was a duty to imagine a world no longer ravaged by senseless wars. His most famous speech was less an invitation to share his epic dream than a commandment.
In these sour, pessimistic times, it is important to remember the great lesson of King’s remarkable life: Impossible dreams can come true.
John Nichols: ‘Right-to-Work’ and the Jim Crow Legacy That Affronts King’s Memory
When the Congress of Industrial Organizations launched “Operation Dixie” in the aftermath of World War II, with the goal not just of organizing unions in the states of the old Confederacy but of ending Jim Crow discrimination, Southern segregationists moved immediately to establish deceptively named “right-to-work” laws.
These measures were designed to make it dramatically harder for workers to organize unions and for labor organizations to advocate for workers on the job site or for social change in their communities and states.
In short order, all the states that had seceded from the Union in order to maintain slavery had laws designed to prevent unions from fighting against segregation. The strategy worked. Southern states have far weaker unions than Northern states, and labor struggles have been far more bitter and violent in the South than in other parts of the country. It was in a right-to-work state, Tennessee, where the Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated while supporting the struggle of African-American sanitation workers to organize a union and have it recognized by the city of Memphis.
Christopher Brauchli: The Senate’s Holiday
Although the Senate is much given to admiring in its members a superiority less obvious or quite invisible to outsiders, one Senator seldom proclaims his own inferiority to another, and still more seldom likes to be told of it.
– Henry Brooks Adams, The Education of Henry AdamsThe Republicans’ newest way of countering criticism that Congress spends more time on recess than it does working occurred when it went home for the Christmas holidays. The criticism occurs because in 2011 Senate and House Members were in session for 112 days, according to the Library of Congress, leaving them 253 days of free time. (These numbers are imprecise. They may have inadvertently worked a few more days than shown.) To counter the impression that they do not work very hard the Republican Senators agreed to pretend they were working when most of them were spending the holidays away from Washington. They agreed that when they were gone they would not be gone.
Jan 16 2012
On this Day In History January 16
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
January 16 is the 16th day of the year in the Gregorian calendar. There are 349 days remaining until the end of the year (350 in leap years).
On this day in 1919, the 18th Amendment to the US Constitution, prohibiting the “manufacture, sale, or transportation of intoxicating liquors for beverage purposes,” is ratified.
The movement for the prohibition of alcohol began in the early 19th century, when Americans concerned about the adverse effects of drinking began forming temperance societies. By the late 19th century, these groups had become a powerful political force, campaigning on the state level and calling for total national abstinence. In December 1917, the 18th Amendment, also known as the Prohibition Amendment, was passed by Congress and sent to the states for ratification.
The amendment and its enabling legislation did not ban the consumption of alcohol, but made it difficult to obtain it legally.
Following significant pressure on lawmakers from the temperance movement, the House of Representatives passed the amendment on December 18, 1917. It was certified as ratified on January 16, 1919, having been approved by 36 states. It went into effect one year after ratification, on January 17, 1920. Many state legislatures had already enacted statewide prohibition prior to the ratification of the Eighteenth Amendment.
When Congress submitted this amendment to the states for ratification, it was the first time a proposed amendment contained a provision setting a deadline for its ratification. The validity of that clause of the amendment was challenged and reached the Supreme Court, which upheld the constitutionality of such a deadline in Dillon v. Gloss (1921).
Because many Americans attempted to evade the restrictions of Prohibition, there was a considerable growth in violent and organized crime in the United States in response to public demand for illegal alcohol. The amendment was repealed by the Twenty-First Amendment on December 5, 1933. It remains the only constitutional amendment to be repealed in its entirety.
To define the language used in the Amendment, Congress enacted enabling legislation called the National Prohibition Act, better known as the Volstead Act, on October 28, 1919. President Woodrow Wilson vetoed that bill, but the House of Representatives immediately voted to override the veto and the Senate voted similarly the next day. The Volstead Act set the starting date for nationwide prohibition for January 17, 1920, which was the earliest date allowed by the 18th Amendment.Volstead Act, on October 28, 1919. President Woodrow Wilson vetoed that bill, but the House of Representatives immediately voted to override the veto and the Senate voted similarly the next day. The Volstead Act set the starting date for nationwide prohibition for January 17, 1920, which was the earliest date allowed by the 18th Amendment.
Jan 15 2012
Rant of the Week: Jon Stewart
Some may quibble with the idea that Newt Gingrich must enter into the bowels of the inner city to explain to black people the power of the paycheck.
Wyatt Cenac analyzes why it took Newt Gingrich so long to be condescending and dickish to African Americans.


Recent Comments