Monday Business Edition
We’ve seen this play before. All of a sudden trillions of dollars of ‘notional’ value turn into meaningless scraps of paper (or ephemeral photons if you prefer) suitable for lining litter boxes or wrapping fish.
Except it’s not even very good at that.
The biggest losers in the casino will turn to taxpayers to make good their losses or simply pretend that they don’t exist. Markets plunge because the trust in magic evaporates and suddenly skeptical children refuse to clap for dying confidence fairies anymore.
Folks, it’s just a fucking light bulb on a string.
Sooner rather than later people are going to take their Greek bets off the table, followed shortly by Spain, Italy, France, and Germany. The Euro will collapse, no longer a threat to the Dollar as a reserve currency. Countries will struggle to rebuild ‘national’ financial systems.
This is all because governments, led by the United States, refused to force banks to deleverage and accept their losses in a timely fashion.
There won’t be another 2008 bailout. In Europe, where there is already violent rioting, Bankers and Ministers will be hung from lamp posts first. In the United States the suicide would be political.
Austerity will not make the losses good either, everything everyone in the bottom 50% owns is a mere $1.4 Trillion. Taking it all won’t solve the problem. Our elites are faced with a decline in their own standard of living that squeezing the poor can’t mitigate.
Good say I.
What will work is more Socialist than Keynesian. Mark to market and vaporize ‘notional’ value. Seize assets and aggressively tax wealth to force investment. Stimulate production by increasing demand.
Real estate values in Greenwich are going to decline and yachts rust in the harbor, but you know, it’s better than selling apples on a street corner worrying that someone is going to cut you for your fancy ass Rolex and that’s next.
The euro zone shuns Geithner
Felix Salmon, Reuters
Sep 16, 2011 16:55 EDT
(I)n sunny Wroclaw, (Geithner) fell spectacularly flat. He waltzed into a meeting of euro zone finance ministers (he took a private car, they shared a bus), and informed them that they should follow his lead and leverage the money in the EFSF. In unison, the finance ministers responded by saying “why, Mr Geithner, that’s a simply spectacular idea, we’re shamefaced to admit that we didn’t think of it ourselves. Thanks for your advice, we’ll follow it, to the letter, forthwith!”
Or, not so much(.)
…
I’m not sure that Geithner was the right person to send to Poland to try to knock European heads together. As the biggest shareholder of the IMF, he would probably have been better off conferring with Christine Lagarde and getting her to make his point for him. The Europeans were never likely to take well to the Americans telling them what to do, especially when their gentle attempts to ask something of Geithner (maybe you might consider getting on board with a financial transactions tax?) were unceremoniously dismissed out of hand by the Treasury secretary.
In any case, Geithner seems to have failed in whatever it was that he was trying to achieve: the only unanimity he managed to foster was in the belief that he had no business telling the euro zone what to do.
EU finance ministers break no new ground on debt crisis
By Jan Strupczewski and Gareth Jones, Reuters
Sat Sep 17, 2011 4:08pm EDT
“He (Geithner) conveyed dramatically that we need to commit money to avoid bringing the system into difficulty,” Austrian Finance Minister Maria Fekter told reporters after the meeting.
“I found it peculiar that even though the Americans have significantly worse fundamental data than the euro zone, they tell us what we should do.”
Geithner also pointed out that euro zone finance ministers could boost the firepower of their bailout fund, the 440 billion euro European Financial Stability Facility, through leveraging.
…
Leveraging would mean that the EFSF could guarantee to cover potential losses of the European Central Bank on purchases of bonds of distressed euro zone sovereigns, boosting the fund’s intervention potential even fivefold, officials said.
…
EU finance ministers also agreed on Saturday that European banks must be strengthened in the follow-up to July stress tests, as a report said a “systemic” crisis in sovereign debt now threatened a new credit crunch.
…
The agreement does not mean European banks are likely to get large, additional capital injections from public coffers — it is just an acknowledgement of the results of the European bank stress tests in July.
The tests showed a financing gap for banks of only 6 billion euros — a sum many investors believe could be much higher if the debt crisis worsens, and which is to be primarily covered by private capital.
Meetings on European Debt Crisis End in Debate, but Little Progress
By STEPHEN CASTLE, The New York Times
Published: September 17, 2011
The meetings were highlighted by the appearance by Timothy F. Geithner, the United States treasury secretary, whose advice, and warnings, drew a tepid reaction from the euro zone’s finance ministers. And Mr. Geithner’s rejection Friday of a European idea for a global tax on financial transactions prompted a debate about whether Europe should go ahead on its own.
…
“The problem is that the politicians seem to be behind the curve all the time,” added Anders Borg, Sweden’s finance minister. “We really need to see some more political leadership,” he said, citing a “clear need for bank recapitalization.”
…
One European official, not authorized to speak publicly, said the ministers “seemed to come to no operational decisions at all.” The only positive news was an outline agreement on new laws to tighten the rulebook for the euro – though that was struck in Brussels.
Saturday’s meeting ended promptly around noon, allowing ministers to leave before a demonstration in Wroclaw against austerity measures in Europe.
Euro Bulls Capitulate After Trichet Turnaround Cuts Forecasts
By Liz Capo McCormick, Lukanyo Mnyanda and Allison Bennett, Bloomberg Business Week
September 18, 2011, 11:22 AM EDT
French President Nicolas Sarkozy and German Chancellor Angela Merkel said Sept. 14 they are “convinced” Greece, which saw yields on its two-year note rise above 80 percent last week, will stay in the currency union, and central banks agreed a day later to lend the region’s financial institutions dollars. While those moves bolstered the euro, the region’s economy has turned weaker, leading traders to bet that the European Central Bank may lower interest rates over the next year instead of raising them, removing a key support for the currency.
…
Mario Blejer, who managed Argentina’s central bank in the aftermath of the world’s biggest sovereign default, said Greece should halt payments on its debt to stop a deterioration of the economy that threatens the EU.
“This debt is unpayable,” Blejer, who was also an adviser to Bank of England Governor Mervyn King from 2003 to 2008, said in an interview last week in Buenos Aires. “Greece should default, and default big. A small default is worse than a big default and also worse than no default.”
…
Even as Europe’s sovereign-debt crisis worsened this year, the euro received support from prospects that the ECB would raise interest rates further to contain inflation. Now, that is looking less likely after ECB President Jean-Claude Trichet said at a press conference in Frankfurt on Sept. 8, after the central bank left its benchmark rate at 1.5 percent, that threats to the euro region have worsened and inflation risks have eased.
…
Officials have contributed to investor skepticism. Bank of France Governor Christian Noyer said on Sept. 12 that French lenders are capable of facing any Greek response to sovereign- debt difficulties and have no liquidity or solvency problems. Two days before Moody’s cut its long-term debt rating by one level Societe Generale’s Chief Executive Officer Frederic Oudea told reporters on Sept. 12 that French banks “have no capital problem.”
“Policy makers and bank leaders have all come out and said ‘everything is fine,’ but clearly everything is not fine,” Louise Cooper, a market analyst at BGC International in London, said in an interview on Sept. 14. “The gap between the rhetoric and what the markets are saying about the level of the crisis is huge.”
Financial Crisis: can the euro hope to survive?
By Martin Vander Weyer, The Telegraph
7:00AM BST 18 Sep 2011
(T)he market bounce was itself an irrational, wishful-thinking response – a misreading of an unprecedentedly dangerous situation. There is a far more persuasive argument that what we have just seen was another week of denial of the reality and imminence of the eurozone’s existential meeting with destiny; another week, to use a currently popular cliché, of kicking the can down the road, rather than facing Europe’s big issues head-on.
Look behind each of the week’s news items and it’s hard not to feel a sense of despair. Geithner was in Wroclaw not to slap his European counterparts on the back for their efforts to date, but to warn them to stop bickering and address the “catastrophic risk” inherent in a widespread state of unsustainable debt and fiscal delinquency.
It is apparent not only that US banks have lost confidence in their European counterparts and have started shutting them out of inter-bank funding markets, but also that US officials are busy making matters worse by seeking to shift blame for America’s dire domestic performance on to influences from this side of the Atlantic. “Seventy-five per cent of the dark things happening in the world economy are because of the eurozone,” one of Geithner’s team said at Marseille.
And it is because of that widely held sentiment in the US financial community – the belief that European banks are sitting on crippling losses on their government bond holdings, and could go down like dominoes if Greece and others default – that the central banks’ dollar funding scheme was necessary to stave off the onset of another credit crunch. Another freezing-up of the international banking system is the quickest possible way to turn current near-zero growth performance in the industrialised world into a global double-dip recession, with the second dip likely to be deeper, longer and more painful than the first.
…
Markets are convinced of several things: that Greece is politically incapable of meeting the austerity demands imposed by the EU and the IMF, and is now locked into a spiral in which its debt position can only become worse as its economy deteriorates; that a default on Greek sovereign debt is therefore inevitable sooner rather than later, and will impose losses on European banks, including the likes of Société Générale and Crédit Agricole of France, which may in turn need to be bailed out by their governments; and that the eviction of a bankrupt and incorrigibly irresponsible eurozone member is not only a technical possibility but an economic necessity if the single currency is to survive at all.
The best hope now is for a managed Greek default and departure. As German transport minister Peter Ramsauer said this week, before Angela Merkel urged him to silence, “it might be risky and painful for Greece to leave the euro, but it would not be the end of the world”.
At the other end of the spectrum, the worst fear is of a final, chaotic Greek episode provoking defaults by Ireland, Portugal and, conceivably, Italy and Spain in its wake. That would be Armageddon – and no one knows what appalling political consequences might follow.
Greek PM cancels U.S. trip as debt crisis deepens
By George Georgiopoulos and Dina Kyriakidou, Reuters
Sun Sep 18, 2011 9:32am IST
Finance Minister Evangelos Venizelos rushed to allay fears the cancelled trip signalled imminent default, saying such talk was “ridiculous”, but the conservative opposition seized the opportunity to demand snap elections, fanning fears Greece lacks the will needed for tough measures ahead.
“The comments and analyses about an imminent default or bankruptcy are not only irresponsible but also ridiculous,” Venizelos said in a statement.
“Every weekend Greece … is subject to this organised attack by speculators in international markets.”
Papandreou was in London, en-route to United Nations and International Monetary Fund (IMF) meetings, when he decided to turn back after discussing developments with Venizelos, government officials said.
From the Desk of Peter Tchir: "Is September 20th Greek Default Day?"
Daniel Alpert, Economonitor
September 17th, 2011
“If Greece is going to default, September 20th seems to be as good a day as any. Actually, it is far better than most to be GD-Day.
Two big bonds, the 4.5% of 2037 and the 4.6% of 2040 both have coupon payments due that day, totalling 769 Million Euro. So if the IMF wanted to avoid letting another billion euro go down the drain, September 20th would be a good day to do it. The IMF seems to have delayed approving another tranche for now, so Greece must already have the money for this payment?
The Fed Scheduled their meeting for 2 days. It now starts on September 20th. Maybe a co-incidence, but what better way to be prepared for new emergency policies?
CDS “rolls” on the 20th. On the 21st, all Sept 2011 CDS will have expired. My guess is that banks own more protection than they sold to the September 20th date, so defaulting while those contracts are still valid would be a net benefit to the banking system. As a whole, triggering CDS will likely benefit banks as I can find banks that say they own protection against positions, but find more hedge funds are uninvolved or have sold protection to fund shorts in other sovereigns.
Suddenly, Over There Is Over Here
By GRETCHEN MORGENSON, The New York Times
Published: September 17, 2011
Billions of dollars in swaps have been written on sovereign debt, guaranteeing that those who bought the insurance will be paid if Greece or other countries default. As of Sept. 9, some $32 billion in net credit insurance exposure was outstanding on debt of Greece, Portugal, Ireland and Spain, according to Markit, a financial data provider. An additional $23.6 billion has been written on Italy’s debt. Billions more in credit insurance have also been written on European banks, many of which hold huge positions in troubled sovereign obligations.
But since these instruments trade in secret, investors don’t know who would be on the hook – as A.I.G. was in its ill-fated mortgage insurance – should a government default or a bank fail.
…
Even after what we went through with A.I.G., the huge market in credit default swaps remains unregulated and still operates in the shadows. You can thank big banks that trade these instruments – and their lobbyists – for that.
…
“We’re seeing a lot of the same things in the markets that we saw in the Lehman era,” Mr. Weinberg said, referring to that awful episode three years ago. “I can’t tell you specifically and exactly how the fallout from Europe will pass through to us, but I certainly can’t tell you it won’t.”

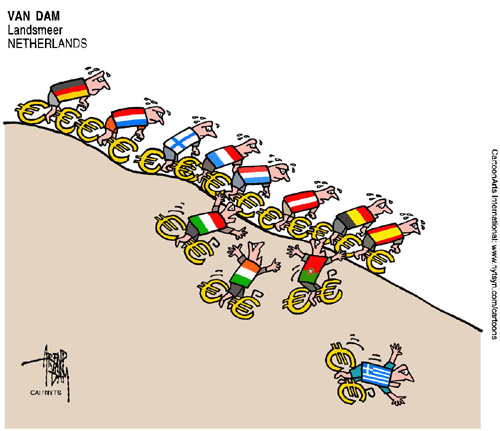 The robust economy of Germany is starting to feel the effects of the economic crisis of its partner nations in the Eurozone and is
The robust economy of Germany is starting to feel the effects of the economic crisis of its partner nations in the Eurozone and is 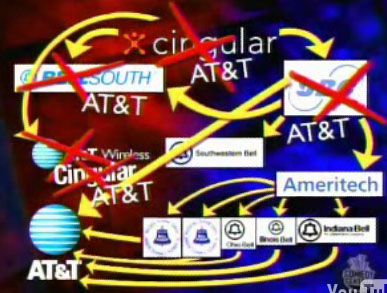 The big business news that hit the “airways” yesterday was the announcement that
The big business news that hit the “airways” yesterday was the announcement that
Recent Comments