 The main purpose our blogging is to communicate our ideas, opinions, and stories both fact and fiction. The best part about the the blogs is information that we might not find in our local news, even if we read it online. Sharing that information is important, especially if it educates, sparks conversation and new ideas. We have all found places that are our favorites that we read everyday, not everyone’s are the same. The Internet is a vast place. Unlike “Punting the Pundits which focuses on opinion pieces mostly from the mainstream media and the larger news web sites, “Around the Blogosphere” will focus more on the medium to smaller blogs and articles written by some of the anonymous and not so anonymous writers and links to some of the smaller pieces that don’t make it to “Pundits” by Krugman, Baker, etc.
The main purpose our blogging is to communicate our ideas, opinions, and stories both fact and fiction. The best part about the the blogs is information that we might not find in our local news, even if we read it online. Sharing that information is important, especially if it educates, sparks conversation and new ideas. We have all found places that are our favorites that we read everyday, not everyone’s are the same. The Internet is a vast place. Unlike “Punting the Pundits which focuses on opinion pieces mostly from the mainstream media and the larger news web sites, “Around the Blogosphere” will focus more on the medium to smaller blogs and articles written by some of the anonymous and not so anonymous writers and links to some of the smaller pieces that don’t make it to “Pundits” by Krugman, Baker, etc.
We encourage you to share your finds with us. It is important that we all stay as well informed as we can.
Follow us on Twitter @StarsHollowGzt
This is an Open Thread.
It takes a gay man to point out the ludicrous hypocrisy and blatant slap in the face to women of the panel of witnesses at this morning’s hearing on military sexual assaults before the Senate Armed Services Committee. From John Aravosis at Americablog:
In a brazen slap in the face to women in the military, the Senate Armed Services Committee – run by Democrats, mind you – invited 18 opponents of legislation addressing sexual assault to testify at a hearing today, while inviting only 2 witnesses who support the sexual assault legislation, and no sexual assault victims at all to testify.
The picture says it all:
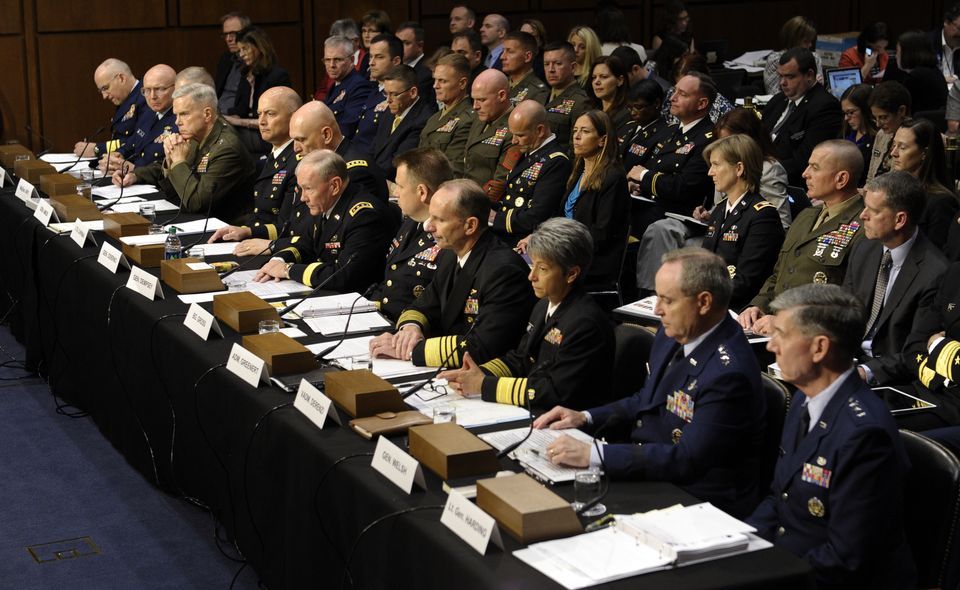

Click on image for the full impact.
At Dependable Renegade, watertiger offers her thoughts on Sen. Saxby Chamblis’ “hormone level created by nature” defense of for rapes in the military for rapes in the military:
What do you call a giant anal sphincter wrapped in worsted wool, ignorance and the American flag? [..]
Remember, this is the guy who (1) avoided serving in Vietnam, and who (2) won election by calling Max Max Cleland, a decorated war veteran who sacrificed mightily for his country, unpatriotic. IOW, Chambliss is a scumbag of the highest order. Asshole Emeritus, even. And a sexist douchebag, to boot. What a guy.
At Corrente, hipparchia has an idea on how to elect more and better Democrats to Congress:
Take a page from the Republican play book: have your candidates for office sign a pledge and then hold them to it.
The pledge? Bring back pork barrel spending. Bring home the Federal dollars to your district or state. Tax the rich to pay for it.
It’s not really a true jobs guarantee program, and it would be a far far better thing if they spend the money on stuff we really need, but even bridges to nowhere provide jobs, plus they’re less morally objectionable than, say, drone manufacturing.
Jim White, at emptywheel, reports of the arrest of an Afghan colonel implicated in atrocities committed by a “shady character” known as Zakaria Kandahari, the CIA and a U.S. special forces team:
In another article at ProPublica, Cora Currier reports “on the death of hundreds, possibly thousands, of Taliban prisoners of war at the hands of U.S.-allied Afghan forces in late 2001.”
I think you know the answer to that question. It’s why John Kiriakou is in prison:
After Obama pledged in 2009 to look into the case, a parallel inquiry was begun the next year in the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, chaired by current Secretary of State John Kerry.
The fate of that investigation is also unclear. The lead investigator, John Kiriakou, was a former CIA officer who was caught up in a criminal leak prosecution and is now in prison. Other Senate staffers could not provide details on Kiriakou’s efforts. Physicians for Human Rights says contact from the committee fizzled out within a year.
Over at Paul Krugman‘s blog Conscious of a Liberal, Paul was at the Princeton commencement this morning. His nephew graduated. Who knew that they still teach Latin?
(T)he high point so far was the Latin salutation, which was apparently – judging from the reactions of those who understood it – a spectacularly funny stand-up routine. Who knew? [..]
Shirley Tilghman has been a great university president, but even I can tell that she speaks Latin with a very Canadian accent.
And this post on Josh Barro’s attempt at being a reasonable conservative and the unintended consequences of the GOP’s Moral Derpitude.
It must be “Pick on Josh Barro Day.” Atrios takes his turn at Eschaton:
On the twitterz earlier Josh Barro wrote:
Liberals love the ARC tunnel that Chris Christie killed bc they love anything with rails, but it was a dumb, overly expensive project.
snip
I’d rather have a $10 billion pair of tunnels than spend $10 billion on equipment the military doesn’t even want. That probably isn’t a choice, either, but we do the latter all of the time. We shouldn’t get “sensible” when the former is an option.
but he did like Josh’s Erickson bashing.
A couple of interesting posts at Yves Smith‘s site, naked capitalism:
The final words go to Charles Pierce at Esquire’s Politics Blog for pointing out this interview with Pentagon Papers whistleblower, Daniel Ellsberg, on MSNBC’s The Cycle about the opening day of PFC Bradley Manning’s court martial.
Ellsberg wasn’t buying the made-to-order prosecutorial three-rail shot from Manning to WikiLeaks to Osama bin Laden.
“It seems absurd and I would say outrageous to say that giving information to the American public and through WikiLeaks to the world and it indicates nothing more than it does give comfort to our actual enemies…these are commentaries on the policies that are actually shameful. I would like to see the people who participated in the atrocities Bradley Manning exposed investigated.”
He’s still pretty sharp.


 Port Royal provided a safe harbour initially for privateers and subsequently for pirates plying the shipping lanes to and from Spain and Panama. Buccaneers found Port Royal appealing for several reasons. Its proximity to trade routes allowed them easy access to prey, but the most important advantage was the port’s proximity to several of the only safe passages or straits giving access to the Spanish Main from the Atlantic. The harbour was large enough to accommodate their ships and provided a place to careen and repair these vessels. It was also ideally situated for launching raids on Spanish settlements. From Port Royal, Henry Morgan attacked Panama, Portobello, and Maracaibo. Roche Brasiliano, John Davis (buccaneer), and Edward Mansveldt (Mansfield) also came to Port Royal.
Port Royal provided a safe harbour initially for privateers and subsequently for pirates plying the shipping lanes to and from Spain and Panama. Buccaneers found Port Royal appealing for several reasons. Its proximity to trade routes allowed them easy access to prey, but the most important advantage was the port’s proximity to several of the only safe passages or straits giving access to the Spanish Main from the Atlantic. The harbour was large enough to accommodate their ships and provided a place to careen and repair these vessels. It was also ideally situated for launching raids on Spanish settlements. From Port Royal, Henry Morgan attacked Panama, Portobello, and Maracaibo. Roche Brasiliano, John Davis (buccaneer), and Edward Mansveldt (Mansfield) also came to Port Royal. The main purpose our blogging is to communicate our ideas, opinions, and stories both fact and fiction. The best part about the the blogs is information that we might not find in our local news, even if we read it online. Sharing that information is important, especially if it educates, sparks conversation and new ideas. We have all found places that are our favorites that we read everyday, not everyone’s are the same. The Internet is a vast place. Unlike “
The main purpose our blogging is to communicate our ideas, opinions, and stories both fact and fiction. The best part about the the blogs is information that we might not find in our local news, even if we read it online. Sharing that information is important, especially if it educates, sparks conversation and new ideas. We have all found places that are our favorites that we read everyday, not everyone’s are the same. The Internet is a vast place. Unlike “





Recent Comments