Author's posts
May 19 2011
On This Day In History May 19
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
May 19 is the 139th day of the year (140th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 226 days remaining until the end of the year.

On this day in 1935, T.E. Lawrence, better known as Lawrence of Arabia, dies from injuries sustained in a motorcycle accident near his home in Dorset, England.
Lieutenant Colonel Thomas Edward Lawrence, CB, DSO (16 August 1888 – 19 May 1935) was a British Army officer renowned especially for his liaison role during the Arab Revolt against Ottoman Turkish rule of 1916-18. The extraordinary breadth and variety of his activities and associations, and his ability to describe them vividly in writing, earned him international fame as Lawrence of Arabia, a title popularised by the 1962 film based on his First World War activities.
Lawrence was born illegitimately in Tremadog, Wales in August 1888 to Sir Thomas Chapman and Sarah Junner, a governess, who was herself illegitimate. Chapman left his wife to live with Sarah Junner, and they called themselves Mr and Mrs Lawrence. In the summer of 1896 the Lawrences moved to Oxford, where from 1907 to 1910 young Lawrence studied history at Jesus College, graduating with First Class Honours. He became a practising archaeologist in the Middle East, working with David George Hogarth and Leonard Woolley on various excavations. In January 1914, following the outbreak of the First World War, Lawrence was co-opted by the British military to undertake a military survey of the Negev Desert while doing archaeological research.
Lawrence’s public image was due in part to American journalist Lowell Thomas‘ sensationalised reportage of the revolt as well as to Lawrence’s autobiographical account Seven Pillars of Wisdom (1922).
At the outbreak of the First World War Lawrence was a university post-graduate researcher who had for years travelled extensively within the Ottoman Empire provinces of the Levant (Transjordan and Palestine) and Mesopotamia (Syria and Iraq) under his own name. As such he became known to the Turkish Interior Ministry authorities and their German technical advisors. Lawrence came into contact with the Ottoman-German technical advisers, travelling over the German-designed, built, and financed railways during the course of his researches.
Even if Lawrence had not volunteered, the British would probably have recruited him for his first-hand knowledge of Syria, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. He was eventually posted to Cairo on the Intelligence Staff of the GOC Middle East.
Contrary to later myth, it was neither Lawrence nor the Army that conceived a campaign of internal insurgency against the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East, but rather the Arab Bureau of Britain’s Foreign Office. The Arab Bureau had long felt it likely that a campaign instigated and financed by outside powers, supporting the breakaway-minded tribes and regional challengers to the Turkish government’s centralised rule of their empire, would pay great dividends in the diversion of effort that would be needed to meet such a challenge. The Arab Bureau had recognised the strategic value of what is today called the “asymmetry” of such conflict. The Ottoman authorities would have to devote from a hundred to a thousand times the resources to contain the threat of such an internal rebellion compared to the Allies’ cost of sponsoring it.
At that point in the Foreign Office’s thinking they were not considering the region as candidate territories for incorporation in the British Empire, but only as an extension of the range of British Imperial influence, and the weakening and destruction of a German ally, the Ottoman Empire.
During the war, Lawrence fought with Arab irregular troops under the command of Emir Faisal, a son of Sherif Hussein of Mecca, in extended guerrilla operations against the armed forces of the Ottoman Empire. He persuaded the Arabs not to make a frontal assault on the Ottoman stronghold in Medina but allowed the Turkish army to tie up troops in the city garrison. The Arabs were then free to direct most of their attention to the Turks’ weak point, the Hejaz railway that supplied the garrison. This vastly expanded the battlefield and tied up even more Ottoman troops, who were then forced to protect the railway and repair the constant damage.
In 1917, Lawrence arranged a joint action with the Arab irregulars and forces under Auda Abu Tayi (until then in the employ of the Ottomans) against the strategically located but lightly defended town of Aqaba. On 6 July, after a surprise overland attack, Aqaba fell to Lawrence and the Arab forces. After Aqaba, Lawrence was promoted to major. Fortunately for Lawrence, the new commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force, General Sir Edmund Allenby, agreed to his strategy for the revolt, stating after the war:
“I gave him a free hand. His cooperation was marked by the utmost loyalty, and I never had anything but praise for his work, which, indeed, was invaluable throughout the campaign.”
Lawrence now held a powerful position, as an adviser to Faisal and a person who had Allenby’s confidence.
The following year, Lawrence was involved in the capture of Damascus in the final weeks of the war and was promoted to lieutenant-colonel in 1918. In newly liberated Damascus-which he had envisioned as the capital of an Arab state-Lawrence was instrumental in establishing a provisional Arab government under Faisal. Faisal’s rule as king, however, came to an abrupt end in 1920, after the battle of Maysaloun, when the French Forces of General Gouraud under the command of General Mariano Goybet http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/M… entered Damascus, breaking Lawrence’s dream of an independent Arabia.
As was his habit when traveling before the war, Lawrence adopted many local customs and traditions (many photographs show him in the desert wearing white Arab dishdasha and riding camels).
During the closing years of the war he sought, with mixed success, to convince his superiors in the British government that Arab independence was in their interests. The secret Sykes-Picot Agreement between France and Britain contradicted the promises of independence he had made to the Arabs and frustrated his work.
In 1918 he co-operated with war correspondent Lowell Thomas for a short period. During this time Thomas and his cameraman Harry Chase shot a great deal of film and many photographs, which Thomas used in a highly lucrative film that toured the world after the war.
Lawrence’s major work is Seven Pillars of Wisdom, an account of his war experiences. In 1919 he had been elected to a seven-year research fellowship at All Souls College, Oxford, providing him with support while he worked on the book. In addition to being a memoir of his experiences during the war, certain parts also serve as essays on military strategy, Arabian culture and geography, and other topics. Lawrence re-wrote Seven Pillars of Wisdom three times; once “blind” after he lost the manuscript while changing trains at Reading railway station.
The list of his alleged “embellishments” in Seven Pillars is long, though many such allegations have been disproved with time, most definitively in Jeremy Wilson‘s authorised biography. However Lawrence’s own notebooks refute his claim to have crossed the Sinai Peninsula from Aqaba to the Suez Canal in just 49 hours without any sleep. In reality this famous camel ride lasted for more than 70 hours and was interrupted by two long breaks for sleeping which Lawrence omitted when he wrote his book.
Lawrence acknowledged having been helped in the editing of the book by George Bernard Shaw. In the preface to Seven Pillars, Lawrence offered his “thanks to Mr. and Mrs. Bernard Shaw for countless suggestions of great value and diversity: and for all the present semicolons.”
The first public edition was published in 1926 as a high-priced private subscription edition, printed in London by Roy Manning Pike and Herbert John Hodgson, with illustrations by Eric Kennington, Augustus John, Paul Nash, Blair Hughes-Stanton and his wife Gertrude Hermes. Lawrence was afraid that the public would think that he would make a substantial income from the book, and he stated that it was written as a result of his war service. He vowed not to take any money from it, and indeed he did not, as the sale price was one third of the production costs. This left Lawrence in substantial debt.
At the age of 46, two months after leaving the service, Lawrence was fatally injured in an accident on his Brough Superior SS100 motorcycle in Dorset, close to his cottage, Clouds Hill, near Wareham. A dip in the road obstructed his view of two boys on their bicycles; he swerved to avoid them, lost control and was thrown over the handlebars. He died six days later on 19 May 1935. The spot is marked by a small memorial at the side of the road.
The circumstances of Lawrence’s death had far-reaching consequences. One of the doctors attending him was the neurosurgeon Hugh Cairns. He was profoundly affected by the incident, and consequently began a long study of what he saw as the unnecessary loss of life by motorcycle dispatch riders through head injuries. His research led to the use of crash helmets by both military and civilian motorcyclists.
Moreton Estate, which borders Bovington Camp, was owned by family cousins, the Frampton family. Lawrence had rented and later bought Clouds Hill from the Framptons. He had been a frequent visitor to their home, Okers Wood House, and had for years corresponded with Louisa Frampton. On Lawrence’s death, his mother arranged with the Framptons for him to be buried in their family plot at Moreton Church. His coffin was transported on the Frampton estate’s bier. Mourners included Winston and Clementine Churchill and Lawrence’s youngest brother, Arnold.
A bust of Lawrence was placed in the crypt at St Paul’s Cathedral and a stone effigy by Eric Kennington remains in the Anglo-Saxon church of St Martin, Wareham
May 19 2011
Playing in Sand on the Economy
This video of an interview with Dean Baker, co-director for the Center for Economic Policy and Research, discussing the debt ceiling and holding the federal budget hostage is a good discussion of what could happen if the debt ceiling is not raised. Baker clearly in the side of raising the debt ceiling but if it comes down to a choice of default and Social Security, he would choose saving Social Security.
There are those who are convinced that the GOP will not allow a default to happen and there has been a lot of pressure from Wall St and banking lobbyists to not play games with this. There is a lot of mistrust that Obama is playing some game that will end up slicing deeply into Social Security and Medicare to make it look as though he had no choice. He does have a choice to insist on a clean bill to raise the debt ceiling and take Social Security and Medicare off the bargaining table. If he doesn’t, as Paul Krugman said, “he might as well move out of the White House, and hand the keys over to the Tea Party.”
May 18 2011
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Wednesday is Ladies’ Day. Scroll down for the Gentlemen
Katrina vanden Heuvel: For-Profit College and the Real Debt Crisis
It’s college commencement season in America, a time of excitement and celebration. For the millions who will graduate this year, the events of this month and next represent not just the end of college but the beginning of a new and meaningful chapter in their lives.
That chapter, for most, however, will be accompanied by hefty student loan payments. According to the Wall Street Journal, the average debt for a bachelor’s degree recipient in 2011 will reach almost $23,000, making this year’s graduating class the most debt-burdened in history. In fact, student loan debt is expected to outpace credit card debt, probably reaching more than $1 trillion this year.
This is partly a function of tuition, which the Wall Street Journal reports has increased at a rate of 5 percent a year. It is also a function of a flailing economy in which parents are far less able to help their children pay for college. It’s no wonder that a staggering 85 percent of 2011 college graduates are moving back home after graduation.
Joan Walsh: Newt Gingrich will never be president
How many racially divisive images and issues can he throw at us in just one week? Keep watching
It’s beginning to look like when Haley Barbour shuffled off into the Mississippi sunset, saying he just couldn’t commit to a 10-year presidential crusade, he left his draft campaign playbook sitting on a garbage can, and Newt Gingrich picked it up. Barbour, you’ll recall, was trying out a new approach to race in the Obama era: Jim Crow wasn’t “that bad,” the white-supremacist White Citizens Councils kept down the KKK, and nobody could make him denounce an effort by the Sons of Confederate Veterans to dedicate a license plate to KKK founder Nathan Bedford Forrest, either. “I don’t go around denouncing people,” declared the man who denounced Democrat Ronnie Musgrove for efforts to remove the Confederate flag from Mississippi’s state flag. I said at the time that Barbour was trying out the notion that post-Obama, people — particularly white people leaning Republican — are ready for an approach that says let’s quit all this whining about racism, it wasn’t that bad, it’s time to get back to the business of cutting taxes for the rich and programs for the poor.
Should the legal arguments over Obama’s health care law force us to reconsider the role of the courts?
It’s hard, nowadays, to begrudge anyone his or her constitutional nihilism. Even before oral arguments started last week over the constitutionality of President Obama’s health care reform law at the federal appeals court in Richmond, Va., some conservatives were complaining that the result was preordained because the three-judge panel consisted of two Obama appointees and a Clinton appointee. And if liberals want to get a head start on their own freak-outs over the lawsuits, they might well note that the just-announced panel for the June 1 hearings on the Affordable Care Act at the 6th Circuit Court of Appeals in Cincinnati include a George W. Bush appointee, a Reagan appointee, and a Carter appointee.
So we can already start writing that 2-1 decision.
Amanda Marcotte: 5 Surprising Things About Sex Women Might Be Scared to Tell Men
Many ballsy women are afraid to say ‘Please do this’ or ‘Don’t do that’ in bed. Here’s what some women are really thinking.
Our sexist culture unleashes many forms of toxic socialization on its inhabitants, but few lessons seem to take as well as teaching girls from the cradle to coddle the male ego, not just with flattery but with a deep unwillingness to speak truths that could cause men to feel uncomfortable or imperfect. And nowhere is this less true than in the sack. Many a woman who feels herself a ballsy broad in her daily life finds herself in bed, afraid to say “Please do this” or “Don’t do that” for fear of confronting a man looking shocked, upset, or disappointed-which can push a button installed in us as little girls labeled Failure As A Woman.
We know we should get over it already. We know we should speak up and take our lumps and men who can’t handle it are bad lovers we should be dumping anyway. It’s not like we’re not trying. The female half of the human race spends an ungodly amount of time and money trying to unlearn passivity and replace it with a dose of speaking up for themselves.
In the meantime, however, there’s a number of things women are thinking about sex that tend to go unsaid, but you men should probably know them anyway.
Robert Reich: The Battle is Squared, and Why We Need Budget Jujitsu
Technically, the federal government has now reached the limit of its capacity to borrow money.
Raising the debt ceiling used to be a technical adjustment, made almost automatically. Now it’s a political football.
Democrats should never have agreed to linking it to an agreement on the long-term budget deficit.
But now that the debt ceiling is in play, there’s no end to what the radical right will demand. John Boehner is already using the classic “they’re making me” move, seemingly helpless in the face of Tea Party storm troopers who refuse to raise the ceiling unless they get their way. Their way is reactionary and regressive – eviscerating Medicare, cutting Medicaid and programs for the poor, slashing education and infrastructure, and using most of the savings to reduce taxes on the rich.
Paul Krugman: Remain Calm: Money Madness Does Not Have to Be Contagious
I’ve been fond of quoting the late economist Charles Kindleberger, my old teacher at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, who used to say that anyone who spends too much time thinking about international money goes mad.
But I’m thinking that we need to expand the proposition: it seems that almost everyone who weighs in on monetary matters of any kind goes crazy.
Those who expected more traction on the United States’ economy from the Federal Reserve’s quantitative easing program are disappointed, but the proper reaction is, “Meh.” Just not a big deal. Similarly for the depreciation of the dollar from its crisis peak to more or less where it was in early 2008 (which has some people hysterical).
John Nichols: From GOP ‘Golden Boy’ To Also-Ran: Paul Ryan’s Big Bad Bummer of a Week
House Budget Committee chairman Paul Ryan, R-Wisconsin, has turned so “toxic” he can’t get away from the protests that began when he came home last month to try to sell his plan to gut Medicare and Medicaid.
And it is starting to cost him politically.
The former “golden boy” of national Republican politics has tarnished his brand to such an extent that, on Tuesday, he had to relinquish his long-cherished dream of running for the U.S. Senate to replace Democratic Senator Herb Kohl.
Kohl is stepping down in 2012 but, after a brief flirtation with the prospect, Ryan signaled that he will skip the contest — effectively giving up on any chance of becoming a senator in the foreseeable future.
Instead, Ryan says, he will focus on trying to revive his budget plan, which after earning an endorsement from House Republicans has stalled in the face of broad national opposition to his proposal to end Medicare and Medicaid as they are known and use the federal money to bail out for-profit insurance companies.
Dean Baker: The Good News and the Bad News in the Social Security Trustees’ Report
There was both good news and bad news in the Social Security trustees’ report released last week. The bad news is that the program is projected to cost somewhat more in the latest report than in the 2010 report.
As a result, its projected 75-year shortfall was increased by 0.3 percentage points of covered payroll from 1.92 percent to 2.22 percent. The year when it was first projected to face a shortfall was moved up a year from 2037 to 2036.
This bad news about the program is also the good news. The main reason that the program’s finances deteriorated between the 2010 report and the 2011 report is that in the 2011 report the trustees assumed that we would enjoy substantially longer life expectancies than they did in the 2010 report.
Jeremy Scahill Erik Prince, You’re No Indiana Jones
When Erik Prince, founder of the infamous mercenary company Blackwater, claimed in early 2010 he was leaving the soldier of fortune business, he said he’d decided to pursue a less dangerous and controversial line of work. “I’m going to teach high school,” he said, straight-faced, in an interview with Vanity Fair. “History and economics. I may even coach wrestling. Hey, Indiana Jones taught school, too.” It was an interesting comment. As fans of Indiana Jones will recall, the whip-wielding archaeologist was indeed a professor. But what he did on the side-traveling the globe in search of potentially history-altering artifacts-was his real passion. In one confrontation with his arch-nemesis, archaeologist René Emile Belloq, who is working for the Nazis, Jones threatens to blow up the Ark of the Covenant with an RPG. “You’re going to give mercenaries a bad name,” Belloq tells him.
Erik Prince did leave the US, but he isn’t teaching high school and is certainly not out of the mercenary business. In fact, far from emerging as a neo-Indiana Jones, the antithesis of a mercenary, Prince is more like Belloq, offering his services to the highest bidder. Over the weekend, The New York Times revealed that Prince was leading an effort to build an army of mercenaries, 800 strong-including scores from Colombia-in Abu Dhabi in the United Arab Emirates. They would be trained by US, European and South African Special Forces veterans. Prince’s new company, Reflex Responses, also known as R2, was bankrolled to the tune of $529 million from “the oil-soaked sheikdom,” according to the Times, adding that Prince was “hired by the crown prince of Abu Dhabi” Sheik Mohamed bin Zayed al-Nahyan. Erik Prince is not mentioned by name in corporate documents outlining the deal, but is instead referred to as “Kingfish.”
May 18 2011
On This Day In History May 18
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
Click on image to enlarge
May 18 is the 138th day of the year (139th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 227 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1917, U.S. Congress passes Selective Service Act.
Some six weeks after the United States formally entered the First World War, the U.S Congress passes the Selective Service Act on May 18, 1917, giving the U.S. president the power to draft soldiers.
When he went before Congress on April 2, 1917, to deliver his war message, President Woodrow Wilson had pledged all of his nation’s considerable material resources to help the Allies-France, Britain, Russia and Italy-defeat the Central Powers. What the Allies desperately needed, however, were fresh troops to relieve their exhausted men on the battlefields of the Western Front, and these the U.S. was not immediately able to provide. Despite Wilson’s effort to improve military preparedness over the course of 1916, at the time of Congress’s war declaration the U.S. had only a small army of volunteers-some 100,000 men-that was in no way trained or equipped for the kind of fighting that was going on in Europe.
To remedy this situation, Wilson pushed the government to adopt military conscription, which he argued was the most democratic form of enlistment. To that end, Congress passed the Selective Service Act, which Wilson signed into law on May 18, 1917. The act required all men in the U.S. between the ages of 21 and 30 to register for military service. Within a few months, some 10 million men across the country had registered in response to the military draft.
During World War I there were three registrations.
The first, on June 5, 1917, was for all men between the ages of 21 and 31.
The second, on June 5, 1918, registered those who attained age 21 after June 5, 1917. A supplemental registration, included in the second registration, was held on August 24, 1918, for those becoming 21 years old after June 5, 1918.
The third registration was held on September 12, 1918, for men age 18 through 45.
After the signing of the armistice of November 11, 1918, the activities of the Selective Service System were rapidly curtailed. On March 31, 1919, all local, district, and medical advisory boards were closed, and on May 21, 1919, the last state headquarters closed operations. The Provost Marshal General was relieved from duty on July 15, 1919, thereby finally terminating the activities of the Selective Service System of World War I.
May 18 2011
Let’s Have A Garage Sale
 Did you know that the Federal government hit the debt ceiling? Did you know that the US government owns 70% of the state of Utah? Did you know that the US government also still has lots of gold in Ft. Knox? The right wing Tea Party Republicans, who now hold the country hostage, have suggested we hold a “garage sale” and sell off assets to pay the ransom.
Did you know that the Federal government hit the debt ceiling? Did you know that the US government owns 70% of the state of Utah? Did you know that the US government also still has lots of gold in Ft. Knox? The right wing Tea Party Republicans, who now hold the country hostage, have suggested we hold a “garage sale” and sell off assets to pay the ransom.
Many conservative Republicans in the House of Representatives, especially those affiliated with the small-government Tea Party movement, say that Geithner and the White House are trying to panic them into raising the debt limit.
They also contend that the Treasury has other options to continue meeting the country’s obligations, such as selling assets including gold reserves and government land.
“There is no certain day,” said congressman James Lankford, a member of the fiscally conservative Republican Study Committee. “It’s a moving target. Even if Aug. 2 is passed, Treasury has the tools in its back pocket to keep us from defaulting.”
Lankford added: “Treasury has done a good job of trying to increase the panic, rather than giving us solutions.”
Dennis Ross, a House Republican and a member of the Tea Party caucus, told Reuters: “I don’t think Treasury has been up front with us. I am not convinced the sky will fall in on August 3.”
Ross added: “I’m not an economist, but I have maintained a household. The federal government owns 70 per cent of Utah, for example. There are federal buildings. If you need cash, let’s start liquidating.”
If they decide to sell off chunks of Nevada, I want first dibs on Area 51.
May 18 2011
Exposing ALEC
No, it’s not an Alec Baldwin expose. This is about The American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) who “owns” and “runs” the US and state governments.
Andrew Gillum, Director of Leadership Programs at People for the American Way Foundation, joins The Last Word to discuss a Republican group more powerful than the Koch brothers.
From People for the American Way
ALEC: The Voice of Corporate Special Interests In State Legislatures
When state legislators across the nation introduce similar or identical bills designed to boost corporate power and profits, reduce workers rights, limit corporate accountability for pollution, or restrict voting by minorities, odds are good that the legislation was not written by a state lawmaker but by corporate lobbyists working through the American Legislative Exchange Council. ALEC is a one-stop shop for corporations looking to identify friendly state legislators and work with them to get special-interest legislation introduced. It’s win-win for corporations, their lobbyists, and right-wing legislators. But the big losers are citizens whose rights and interests are sold off to the highest bidder.
The American Legislative Exchange Council (ALEC) was founded in 1973 by Paul Weyrich, who helped build a nationwide right-wing political infrastructure following the reelection of Richard Nixon. In the same year, he helped establish the Heritage Foundation, now one of the most prominent right-wing policy institutes in the country. One year later, Weyrich founded the Committee for the Survival of a Free Congress, the predecessor of the Free Congress Foundation. In 1979, he co-founded and coined the Moral Majority with Jerry Falwell, and in 1981 he helped establish the ultraconservative Council on National Policy.
May 17 2011
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Paul Krugman: America Held Hostage
Six months ago President Obama faced a hostage situation. Republicans threatened to block an extension of middle-class tax cuts unless Mr. Obama gave in and extended tax cuts for the rich too. And the president essentially folded, giving the G.O.P. everything it wanted.
Now, predictably, the hostage-takers are back: blackmail worked well last December, so why not try it again? This time House Republicans say they will refuse to raise the debt ceiling – a step that could inflict major economic damage – unless Mr. Obama agrees to large spending cuts, even as they rule out any tax increase whatsoever. And the question becomes what, if anything, will get the president to say no.
Chris Hedges: The Obama Deception: Why Cornel West Went Ballistic
No one grasps this tragic descent better than West, who did 65 campaign events for Obama, believed in the potential for change and was encouraged by the populist rhetoric of the Obama campaign. He now nurses, like many others who placed their faith in Obama, the anguish of the deceived, manipulated and betrayed. He bitterly describes Obama as “a black mascot of Wall Street oligarchs and a black puppet of corporate plutocrats. And now he has become head of the American killing machine and is proud of it.”
“When you look at a society you look at it through the lens of the least of these, the weak and the vulnerable; you are committed to loving them first, not exclusively, but first, and therefore giving them priority,” says West, the Class of 1943 University Professor of African American Studies and Religion at Princeton University. “And even at this moment, when the empire is in deep decline, the culture is in deep decay, the political system is broken, where nearly everyone is up for sale, you say all I have is the subversive memory of those who came before, personal integrity, trying to live a decent life, and a willingness to live and die for the love of folk who are catching hell. This means civil disobedience, going to jail, supporting progressive forums of social unrest if they in fact awaken the conscience, whatever conscience is left, of the nation. And that’s where I find myself now.”
It’s almost enough to give socialism a bad name.
We don’t know whether Dominique Strauss-Kahn – who heads the International Monetary Fund and, until a few days ago, was likely to be the Socialist Party candidate for president of France – is guilty of the alleged sexual assault for which he was arrested. Like anyone, he is presumed innocent until court proceedings prove otherwise.
We do know, however, that at the time of the reported incident on Saturday, Strauss-Kahn was resident in a $3,000-a-night luxury suite at a posh midtown Manhattan hotel. We also know that when he was taken into police custody hours later, aboard a Paris-bound jetliner that was moments from takeoff at John F. Kennedy International Airport, police found him comfortably ensconced in the first-class cabin.
I didn’t think this was how socialists were supposed to roll.
Laurence Lewis: Of Abbottabad: The questions are more important than the answers
There has been much debate and discussion over the nature of President Obama’s order that led to the killing of Osama bin Laden at Abbottabad. Based on different reporting, different people claim to know for a fact that it was a kill order, a kill-or-capture, or a capture-or-kill. And but for those involved in the raid, the truth probably won’t be known for many years. It is the seeking that is most interesting. As if knowing the nature of the order will establish some level of moral clarity. And as is too often the case, many seem to want such clarity mostly for personality-based reasons- to understand or cast judgment upon the president and his staff, or even the people with whom they are arguing. But lost amidst many of these personality arguments are the larger moral issues themselves. What does it say if the president did order a kill rather than a capture-or-kill? Many would have supported such an order in the first place, so for them the truth shouldn’t much matter beyond establishing historical accuracy. But many would not have supported such an order. And that is where the real source of discussion ought to begin.
Robert Parry: Mitch Daniels, Architect of US Debt Crisis
To hear Official Washington tell it, Indiana Gov. Mitch Daniels is the new “serious” Republican presidential contender. He’s praised as a “fiscal conservative” who isn’t obsessed with the Right’s divisive social agenda nor marred by the crazy “birther” conspiracy theories.
Mentioned only in passing is a key fact that – in a saner world – would disqualify him from holding any government office: Mitch Daniels was President George W. Bush’s original budget director in 2001.
In other words, the “fiscal conservative” Daniels oversaw the federal budget as it was making its precipitous dive from a $236 billion surplus – then on a trajectory to eliminate the entire federal debt in a decade – to a $400 billion deficit by the time he left in June 2003.
Plus, because of proposals developed on Daniels’s watch – such as tax cuts favoring the rich and unpaid-for projects, including the invasion of Iraq and a new prescription drug plan – the fiscal situation of the federal government continued to sink over the ensuing years, plunging to a trillion-dollar-plus annual deficit by the time Bush left office in 2009.
John Nichols: Tens of Thousands Rally in Wisconsin to Declare: “This Fight is NOT Over!”
Protest fatigue? Not in Wisconsin.
Three months after Governor Scott Walker proposed to strip state, county and municipal employees and public-school teachers of their collective bargaining rights, the governor’s agenda remains stymied. Legal challenges,moves to recall Republican legislators who have sided with the governor and the fear on the part of legislative leaders of mass protests have prevented implementation.
That fear is well-founded.
The Wisconsin protests have inspired similar demonstrations in states across the country, including state Capitol confrontations in Indiana, Massachusetts, Michigan, Ohio and, most recently, California and New York.
Yet, the energy in Wisconsin remains unmistakable, and unrelenting.
Michael Keegan: State Budget Battles are about More than Cutting Deficits
Assaults on middle-class Americans are spreading rapidly.
Earlier this year, people across the country were riveted to the politics of Wisconsin. Claiming to address the state’s budget crisis, Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker proposed eliminating the right of public workers to unionize. Wisconsin’s citizens immediately took to the streets in massive protests – only to see the union-busting legislation pushed through by the state senate in a late-night surprise vote. Although Madison’s capitol building is now cleared and most of the news teams have bolted, the issue of public unions is far from over in Wisconsin. Meanwhile, it has just begun for the rest of the country.
The dire budgetary situations many states find themselves in are real problems, and they require real solutions. But some state leaders are proposing “solutions” that are forcing social policy shifts and making political power plays that will do nothing to reduce deficits.
May 17 2011
On This Day In History May 17
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
Click on image to enlarge
May 17 is the 137th day of the year (138th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 228 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1954, in a major civil rights victory, the U.S. Supreme Court hands down an unanimous decision in Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, ruling that racial segregation in public educational facilities is unconstitutional. The historic decision, which brought an end to federal tolerance of racial segregation, specifically dealt with Linda Brown, a young African American girl who had been denied admission to her local elementary school in Topeka, Kansas, because of the color of her skin.
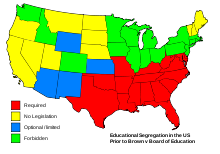
Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka, 347 U.S. 483 (1954), was a landmark decision of the United States Supreme Court that declared state laws establishing separate public schools for black and white students unconstitutional. The decision overturned the Plessy v. Ferguson decision of 1896 which allowed state-sponsored segregation. Handed down on May 17, 1954, the Warren Court’s unanimous (9-0) decision stated that “separate educational facilities are inherently unequal.” As a result, de jure racial segregation was ruled a violation of the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment of the United States Constitution. This ruling paved the way for integration and the civil rights movement.
The case of Brown v. Board of Education as heard before the Supreme Court combined five cases: Brown itself, Briggs v. Elliott (filed in South Carolina), Davis v. County School Board of Prince Edward County (filed in Virginia), Gebhart v. Belton (filed in Delaware), and Bolling v. Sharpe (filed in Washington D.C.).
All were NAACP-sponsored cases. The Davis case, the only case of the five originating from a student protest, began when sixteen-year-old Barbara Rose Johns organized and led a 450-student walkout of Moton High School.
The Kansas case was unique among the group in that there was no contention of gross inferiority of the segregated schools’ physical plant, curriculum, or staff. The district court found substantial equality as to all such factors. The Delaware case was unique in that the District Court judge in Gebhart ordered that the black students be admitted to the white high school due to the substantial harm of segregation and the differences that made the schools separate but not equal. The NAACP’s chief counsel, Thurgood Marshall, who was later appointed to the U.S. Supreme Court in 1967, argued the case before the Supreme Court for the plaintiffs. Assistant attorney general Paul Wilson, later distinguished emeritus professor of law at the University of Kansas, conducted the state’s ambivalent defense in his first appellate trial.
Unanimous Opinion and Key Holding
In spring 1953 the Court heard the case but was unable to decide the issue and asked to rehear the case in fall 1953, with special attention to whether the Fourteenth Amendment’s Equal Protection Clause prohibited the operation of separate public schools for whites and blacks.
The case was being reargued at the behest of Associate Justice Felix Frankfurter, who used re-argument as a stalling tactic, to allow the Court to gather a unanimous consensus around a Brown opinion that would outlaw segregation. Chief Justice Vinson had been a key stumbling block. The justices in support of desegregation spent much effort convincing those who initially dissented to join a unanimous opinion. Even though the legal effect would be same for a majority versus unanimous decision, it was felt that it was vital to not have a dissent which could be relied upon by opponents of desegregation as a legitimizing counterargument.
Conference notes and draft decisions illustrate the division of opinions before the decision was issued. Justices Douglas, Black, Burton, and Minton were predisposed to overturn Plessy. Fred M. Vinson noted that Congress had not issued desegregation legislation; Stanley F. Reed discussed incomplete cultural assimilation and states’ rights and was inclined to the view that segregation worked to the benefit of the African-American community; Tom C. Clark wrote that “we had led the states on to think segregation is OK and we should let them work it out.” Felix Frankfurter and Robert H. Jackson disapproved of segregation, but were also opposed to judicial activism and expressed concerns about the proposed decision’s enforceability. After Vinson died in September 1953, President Dwight D. Eisenhower appointed Earl Warren as Chief Justice. Warren had supported the integration of Mexican-American students in California school systems following Mendez v. Westminster.
While all but one justice personally rejected segregation, the self-restraint faction questioned whether the Constitution gave the Court the power to order its end. The activist faction believed the Fourteenth Amendment did give the necessary authority and were pushing to go ahead. Warren, who held only a recess appointment, held his tongue until the Senate, dominated by southerners, confirmed his appointment.
Warren convened a meeting of the justices, and presented to them the simple argument that the only reason to sustain segregation was an honest belief in the inferiority of Negroes. Warren further submitted that the Court must overrule Plessy to maintain its legitimacy as an institution of liberty, and it must do so unanimously to avoid massive Southern resistance. He began to build a unanimous opinion.
Although most justices were immediately convinced, Warren spent some time after this famous speech convincing everyone to sign onto the opinion. Justices Robert Jackson and Stanley Reed finally decided to drop their dissent to what was by then an opinion backed by all the others. The final decision was unanimous. Warren drafted the basic opinion and kept circulating and revising it until he had an opinion endorsed by all the members of the Court.
The key holding of the Court was that, even if segregated black and white schools were of equal quality in facilities and teachers, segregation by itself was harmful to black students and unconstitutional. They found that a significant psychological and social disadvantage was given to black children from the nature of segregation itself, drawing on research conducted by Kenneth Clark assisted by June Shagaloff. This aspect was vital because the question was not whether the schools were “equal”, which under Plessy they nominally should have been, but whether the doctrine of separate was constitutional. The justices answered with a strong “no”:
Does segregation of children in public schools solely on the basis of race, even though the physical facilities and other “tangible” factors may be equal, deprive the children of the minority group of equal educational opportunities? We believe that it does… Segregation of white and colored children in public schools has a detrimental effect upon the colored children. The impact is greater when it has the sanction of the law, for the policy of separating the races is usually interpreted as denoting the inferiority of the negro group. A sense of inferiority affects the motivation of a child to learn. Segregation with the sanction of law, therefore, has a tendency to [retard] the educational and mental development of negro children and to deprive them of some of the benefits they would receive in a racial[ly] integrated school system… We conclude that, in the field of public education, the doctrine of “separate but equal” has no place. Separate educational facilities are inherently unequal. Therefore, we hold that the plaintiffs and others similarly situated for whom the actions have been brought are, by reason of the segregation complained of, deprived of the equal protection of the laws guaranteed by the Fourteenth Amendment.
May 17 2011
Presidential Elections French Style
 The arrest of IMF President Dominique Strauss-Kahn in New York City on sexual assault charges puts on interesting twist on the French Presidential Elections. He is finished as head of the IMF and most certainly washed up with politics in France whether he is acquitted of these charges or not. The French like their sex but not necessarily on the front page of every newspaper around the world. This leaves a gaping hole for the Socialist Party (Parti Socialiste) of whom M. Strauss-Kahn, known as DSK in France, was the leading candidate and was expected to defeat President Nicholas Sarkozy.
The arrest of IMF President Dominique Strauss-Kahn in New York City on sexual assault charges puts on interesting twist on the French Presidential Elections. He is finished as head of the IMF and most certainly washed up with politics in France whether he is acquitted of these charges or not. The French like their sex but not necessarily on the front page of every newspaper around the world. This leaves a gaping hole for the Socialist Party (Parti Socialiste) of whom M. Strauss-Kahn, known as DSK in France, was the leading candidate and was expected to defeat President Nicholas Sarkozy.
The French Presidential elections are held every 5 years in April, separately from the legislative election for the two chamber Parlement (Parliament). France does not have a two party system but a system where, though many political parties exist, only two parties have a chance of getting elected to major positions. Power, however, usually passes back and forth between the two stablest coalitions representing the left and the right.
Between now and next fall there will be primaries among the opposition parties where there are more than one declared candidate. The Front National’s (FN) primary was held January 11th, electing its president, Marine Le Pen, the youngest daughter of Jean-Marie Le Pen, former president of the FN, to be their candidate. The Parti Socialiste will hold their primary on June 28th with multiple candidates. Pres. Sarkozy, who is backed by Union Pour Un Mouvement Populaire (UMP), already has their endorsement.
The Socialist Party will now have to choose among several likely candidates who may have the popular support to take the Elysée Palace next year. The damage of the DSK affair may weaken the left, and the beneficiary will not be the ruling UMP party. It has been speculated that, both as a political “outsider” and as a woman in politics, Marine Le Pen could gain most from the scandal.
The other “dark horse” to watch is the former First Secretary of the Socialist Party and former partner of Ségolène Royal, François Hollande. In recent weeks, Mr Hollande has made strong gains in polls, with some analysts suggesting he could represent an even greater threat to the UMP president than the IMF boss did when he was popular. DSK’s was seen as an “elitist” whose policies resembled those of Pres. Sarkozy, while M. Hollande is more to the left and very much a “man of the people”. He still faces the primary with the current First Secretary of the Socialist Party, Martine Aubry, President of the Regional Council of Poitou-Charentes, Ségolène Royal (who lost to Sarkozy in 2007), President of the General Council of Saône-et-Loire and MP, Arnaud Montebourg and Essonne MP and Mayor of Évry, Manuel Valls.
I’ve simplified this a bit, the system is not all that complicated. French politics are really not all that different from American politics except that the French, as most Europeans, do not consider their politician’s private lives or religion a factor in considering who would be the best to lead the country. Feel free to ask questions, I’ll answer as best I can.
May 16 2011
The Reason We Need Wikileaks
 Now more than ever, the reason for Wikileaks to exist: the preservation of what remains of the rule of law and the US Constitution. From Marcy Wheeler at FDL:
Now more than ever, the reason for Wikileaks to exist: the preservation of what remains of the rule of law and the US Constitution. From Marcy Wheeler at FDL:
SCOTUS: Govt Can Use State Secrets to Hide Crimes
SCOTUS just declined to take the Jeppesen Dataplan suit.
The high court rejected an appeal by five men who claimed that U.S. operatives-with support from Jeppesen Dataplan Inc., a Boeing unit-abducted them and sent them to other countries where they were tortured. They alleged Jeppesen provided critical flight planning and logistical support to the CIA’s “extraordinary rendition” program. The men were seeking unspecified monetary damages from the company.
This effectively means that men like Binyam Mohamed, who the Brits have admitted was tortured after being rendered, cannot sue for redress. And the ruling is particularly egregious since a Jeppesen executive admitted that his company was flying rendition flights.
In effect, SCOTUS’ decision not to take this case leaves in place state secrets precedent that allows the government to commit grave crimes, but hide behind state secrets.
Update: The Brennan Center and a bunch of other crazy hippies who believe in rule of law wrote a letter in response to SCOTUS’ decision to DOJ reminding them that, per their purported state secrets policy, credible allegations of wrong-doing must be referred to the Inspectors General of the relevant agencies for investigation.
snip
This is me officially holding my breath for the Obama Administration to do what they promised on this front.
Don’t hold your breath, Marcy. I have no expectations of the Obama administrations doing anything they promised regarding the rule of law and the Constitution. Dick Cheney must be proud.


Recent Comments