“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Peter Daou: Resolving the “Obama Paradox” (The Most Successful Failed Presidency in a Generation)
The intense dispute over President Obama’s personality, principles and policies is a proxy for the larger debate over the history, values, ideological composition and direction of America. The focus is on the person, but the battle is over the nation.
In that context, a number of progressive activists and observers (this writer included) have spent the past 18 months repeatedly making the case that the Obama administration’s unwillingness to stake out a strong, principled, progressive position on key issues is detrimental to Obama’s political fortunes, to the Democratic Party’s electoral prospects and most importantly, to the country. Looking at polls, trends, midterm projections, the economy, the environment, the war in Afghanistan, etc., the facts on the ground appear to have borne out that view.
snip
Further, the definitions of success and failure that undergird the “Obama Paradox” are exceedingly amorphous. Is it about legislative wins, no matter the underlying substance? Is it public opinion as reflected in polls? Is it pundit consensus and conventional wisdom?
And who defines success or judges which issue or question is the most important? Is it jobs? The Gulf disaster? Health care? Is Obama a progressive, a centrist, a corporatist, a socialist? Are we winning or losing Afghanistan? Is Obama the next FDR, Bush-lite, the anti-Bush, or the un-Reagan?
snip
So how do we resolve the present contradictions surrounding President Obama and how do we make a fair assessment of his tenure? To the extent that we can, we do so by clarifying our approach in advance of our judgment. A reporter looking at facts and data should first choose the metric(s). It might be the number of campaign promises kept, or legislation passed, or public opinion polls and trends, or economic stats, or a weighted combination of several factors.
For activists and opinion-makers, the process is somewhat different: it’s about fundamental ideals and values against which the president’s actions are measured.
For the general public, it’s a mix of personal circumstances (how the administration’s policies affect them and their families), their values, what the media tells them, what their friends and family think, and so on.
Whatever the parameters and methods, there are several ways to reach an informed, albeit incomplete, view of Obama’s presidency. Naturally, some of these views will be contradictory. From certain perspectives Obama is successful, from others he’s not – there’s nothing paradoxical about that.
What’s far more interesting is that there is one thing Obama can do that transcends the ebb and flow of events, the endless swirl of opinion, the daily wins and losses, the progress and setbacks that constitute governing. It is the one thing with lasting appeal and enduring value and a prerequisite for unqualified success in any endeavor: standing for something worthwhile, for a set of well-articulated principles, and fighting for those principles tooth and nail.
The real Obama paradox is why that hasn’t happened when it’s good policy and good politics.

 Five years after General George A. Custer’s infamous defeat at the Battle of Little Bighorn, Hunkpapa Teton Sioux leader Sitting Bull surrenders to the U.S. Army, which promises amnesty for him and his followers. Sitting Bull had been a major leader in the 1876 Sioux uprising that resulted in the death of Custer and 264 of his men at Little Bighorn. Pursued by the U.S. Army after the Indian victory, he escaped to Canada with his followers.
Five years after General George A. Custer’s infamous defeat at the Battle of Little Bighorn, Hunkpapa Teton Sioux leader Sitting Bull surrenders to the U.S. Army, which promises amnesty for him and his followers. Sitting Bull had been a major leader in the 1876 Sioux uprising that resulted in the death of Custer and 264 of his men at Little Bighorn. Pursued by the U.S. Army after the Indian victory, he escaped to Canada with his followers.

 Welcome to the Stars Hollow Health and Fitness weekly diary. It will publish on Saturday afternoon and be open for discussion about health related issues including diet, exercise, health and health care issues, as well as, tips on what you can do when there is a medical emergency. Questions are encouraged and I will answer to the best of my ability. If I can’t, I will try to steer you in the right direction. Naturally, I cannot give individual medical advice for personal health issues. I can give you information about medical conditions and the current treatments available.
Welcome to the Stars Hollow Health and Fitness weekly diary. It will publish on Saturday afternoon and be open for discussion about health related issues including diet, exercise, health and health care issues, as well as, tips on what you can do when there is a medical emergency. Questions are encouraged and I will answer to the best of my ability. If I can’t, I will try to steer you in the right direction. Naturally, I cannot give individual medical advice for personal health issues. I can give you information about medical conditions and the current treatments available.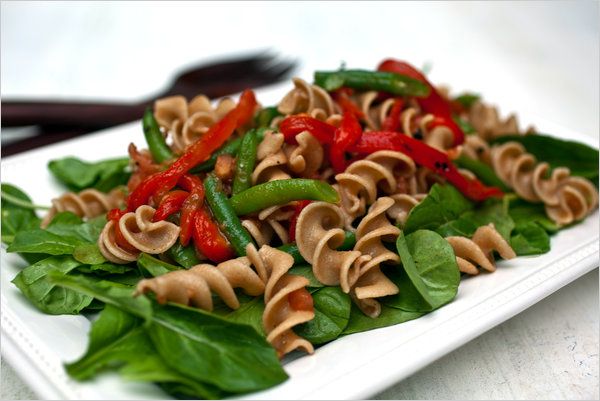 


Recent Comments