This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
October 18 is the 291st day of the year (292nd in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 74 days remaining until the end of the year.
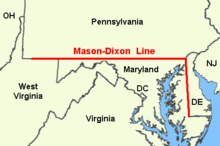
On this day in 1767, Mason and Dixon Draw a line.
Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon complete their survey of the boundary between the colonies of Pennsylvania and Maryland as well as areas that would eventually become the states of Delaware and West Virginia. The Penn and Calvert families had hired Mason and Dixon, English surveyors, to settle their dispute over the boundary between their two proprietary colonies, Pennsylvania and Maryland.
In 1760, tired of border violence between the colonies’ settlers, the British crown demanded that the parties involved hold to an agreement reached in 1732. As part of Maryland and Pennsylvania’s adherence to this royal command, Mason and Dixon were asked to determine the exact whereabouts of the boundary between the two colonies. Though both colonies claimed the area between the 39th and 40th parallel, what is now referred to as the Mason-Dixon line finally settled the boundary at a northern latitude of 39 degrees and 43 minutes. The line was marked using stones, with Pennsylvania’s crest on one side and Maryland’s on the other.
Background
Maryland’s charter granted the land north of the entire length of the Potomac River up to the 40th parallel. A problem arose when Charles II granted a charter for Pennsylvania. The grant defined Pennsylvania’s southern border as identical to Maryland’s northern border, the 40th parallel. But the terms of the grant clearly indicate that Charles II and William Penn assumed the 40th parallel would intersect the Twelve-Mile Circle around New Castle, Delaware when in fact it falls north of Philadelphia, the site of which Penn had already selected for his colony’s capital city. Negotiations ensued after the problem was discovered in 1681. A compromise proposed by Charles II in 1682, which might have resolved the issue, was undermined by Penn receiving the additional grant of the ‘Three Lower Counties’ along Delaware Bay, which later became the Delaware Colony, a satellite of Pennsylvania. These lands had been part of Maryland’s original grant.
In 1732 the proprietary governor of Maryland, Charles Calvert, 5th Baron Baltimore, signed a provisional agreement with William Penn’s sons which drew a line somewhere in between, and also renounced the Calvert claim to Delaware. But later Lord Baltimore claimed that the document he signed did not contain the terms he had agreed to, and refused to put the agreement into effect. Beginning in the mid-1730s, violence erupted between settlers claiming various loyalties to Maryland and Pennsylvania. The border conflict between Pennsylvania and Maryland would be known as Cresap’s War.
The issue was unresolved until the Crown intervened in 1760, ordering Frederick Calvert, 6th Baron Baltimore to accept the 1732 agreement. Maryland’s border with Delaware was to be based on the Transpeninsular Line and the Twelve-Mile Circle around New Castle. The Pennsylvania-Maryland border was defined as the line of latitude 15 miles south of the southernmost house in Philadelphia.
As part of the settlement, the Penns and Calverts commissioned the English team of Charles Mason and Jeremiah Dixon to survey the newly established boundaries between the Province of Pennsylvania, the Province of Maryland, Delaware Colony, and parts of Colony and Old Dominion of Virginia.
After Pennsylvania abolished slavery in 1781, the western part of this line and the Ohio River became a border between free and slave states, although Delaware remained a slave state.




Recent Comments