Author's posts
Apr 27 2012
The Good, the Bad and That Dead Fairy
The Confidence Fairy is Dead but its ghost is still haunting the halls of the European Union countries and the United States, as Herr Doktor notes:
This was the month the confidence fairy died.
For the past two years most policy makers in Europe and many politicians and pundits in America have been in thrall to a destructive economic doctrine. [..]
The good news is that many influential people are finally admitting that the confidence fairy was a myth. The bad news is that despite this admission there seems to be little prospect of a near-term course change either in Europe or here in America, where we never fully embraced the doctrine, but have, nonetheless, had de facto austerity in the form of huge spending and employment cuts at the state and local level.
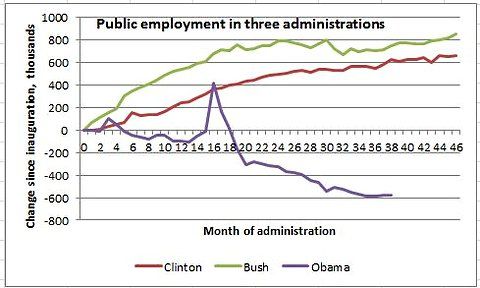
Krugman also pointed the de facto austerity policy of the Obama administration and Congress have added to the stagnant job market:
Here’s a comparison of changes in government employment (federal, state, and local) during the first four years of three presidents who came to office amid a troubled economy:
That spike early on is Census hiring; [..] If public employment had grown the way it did under Bush, we’d have 1.3 million more government workers, and probably an unemployment rate of 7 percent or less.
The job market is taking its toll on consumer spending which will continue to slow down any recovery:
More Americans than forecast filed applications for unemployment benefits last week and consumer confidence declined by the most in a year, signaling that a cooling labor market may restrain household spending. [..]
“There has been some slowdown in the labor market,” said Yelena Shulyatyeva, a U.S. economist at BNP Paribas in New York, who correctly projected the level of jobless claims. “That makes consumers feel less confident, and makes them more cautious about their spending. We could see some weakness in April payrolls.”
And even though the predictions about the housing market have been optimistic don’t be fooled, there is a dark side as falling home prices drag new buyers under water
More than 1 million Americans who have taken out mortgages in the past two years now owe more on their loans than their homes are worth, and Federal Housing Administration loans that require only a tiny down payment are partly to blame.
That figure, provided to Reuters by tracking firm CoreLogic, represents about one out of 10 home loans made during that period.
It is a sobering indication the U.S. housing market remains deeply troubled, with home values still falling in many parts of the country, and raises the question of whether low-down payment loans backed by the FHA are putting another generation of buyers at risk.
As of December 2011, the latest figures available, 31 percent of the U.S. home loans that were in negative equity – in which the outstanding loan balance exceeds the value of the home – were FHA-insured mortgages, according to CoreLogic.
In an interview with The European Nobel Prize winning economist, Joseph Stiglitz said:
…When you look at America, you have to concede that we have failed. Most Americans today are worse off than they were fifteen years ago. A full-time worker in the US is worse off today than he or she was 44 years ago. That is astounding – half a century of stagnation. The economic system is not delivering. It does not matter whether a few people at the top benefitted tremendously – when the majority of citizens are not better off, the economic system is not working… [..]
The argument that the response to the current crisis has to be a lessening of social protection is really an argument by the 1% to say: “We have to grab a bigger share of the pie.” But if the majority of people don’t benefit from the economic pie, the system is a failure. I don’t want to talk about GDP anymore, I want to talk about what is happening to most citizens.
Meanwhile back in Europe with the distinct possibility that French President Nicholas Sarkozy may lose to the Socialist candidate François Hollande, some leaders are getting the message but aren’t ready to give up totally:
Dutch Prime Minister Mark Rutte and Finance Minister Jan Kees de Jager struck a deal with the opposition and got a majority backing on an austerity package to meet the 3 percent budget deficit target in 2013, after seven weeks of talks with Geert Wilders’s Freedom Party failed and led to the collapse of the minority government.
The package increases the value-added tax to 21 percent from 19 percent, doubles the bank tax to 600 million euros ($791 million) and changes the financing of mortgages, De Jager said in a letter to parliament yesterday.[..]
The Labor Party, the Socialist Party as well as the Freedom Party of Geert Wilders didn’t back the agreement. “This is a bad package and the people with a state pension will pay the bill,” Wilders said in parliament.
In an editorial in Bloomberg News, the editors expressed their ideas how European leaders can “boost economic growth in the euro area”:
First, Europe’s leaders must recognize that common deficit rules alone will not guarantee the currency union’s survival. When countries such as Italy and Spain fall into a spiral of shrinking output and rising budget deficits, countries with stronger economies must be willing to help, either by transferring funds or by stimulating their own demand.
Currently, that would mean more German spending. [..] The Bundesbank would also need to live with a little more German inflation than the current 2.1 percent. Higher prices in Germany would help make other euro- area economies and their exports more competitive, reducing both their current account deficits and Germany’s surplus.
Second, the agreement should give Spain and Greece in particular more time to bring down debts piled up over the past 30 years. Requiring them to slash education, research and development, and other budgets will only stunt their future growth potential. To calm markets concerned about Spain’s deficits, the rest of Europe — Germany again — and the International Monetary Fund would have to provide more bailout funds.
Finally, the pact should acknowledge one of the most immediate requirements for a return to economic expansion: Recapitalization of private sector banks so that they can start providing businesses with more credit. Without that, Europe is doomed to anemic growth and a persistent confidence crisis, no matter what documents its politicians may sign.
Stiglitz in his interview makes two important points. First, “The question of social protection does not have to do with the structure of production”
It has to do with social cohesion or solidarity. That is why I am also very critical of Draghi’s argument at the European Central Bank that social protection has to be undone. There are no grounds upon which to base that argument. The countries that are doing very well in Europe are the Scandinavian countries. Denmark is different from Sweden, Sweden is different from Norway – but they all have strong social protection and they are all growing.
Hear that, Mr President and Congress? Get your hands off reduction in the social safety net.
And second, that here in the US, “politics is at the root of the problem“:
Most Americans understand that fraud political processes play in fraud outcomes. But we don’t know how to break into that system. Our Supreme Court was appointed by moneyed interests and – not surprisingly – concluded that moneyed interests had unrestricted influence on politics. In the short run, we are exacerbating the influence of money, with negative consequences for the economy and for society. [..]
The diagnosis is that politics is at the root of the problem: That is where the rules of the game are made, that is where we decide on policies that favor the rich and that have allowed the financial sector to amass vast economic and political power. The first step has to be political reform: Change campaign finance laws. Make it easier for people to vote – in Australia, they even have compulsory voting. Address the problem of gerrymandering. Gerrymandering makes it so that your vote doesn’t count. If it does not count, you are leaving it to moneyed interests to push their own agenda. Change the filibuster, which turned from a barely used congressional tactic into a regular feature of politics. It disempowers Americans. Even if you have a majority vote, you cannot win.
The Europeans may well be the “game changers” because the election of their politicians doesn’t hinge on campaign contributions, long drawn out primaries or a rigid two party system that has degenerated into a lack of political choice. We need to kill the fairy once and for all and put governance in the hands of the American people.
Apr 26 2012
The French Presidential Election 2012: A Rejecting of Austerity?
 With the first round of elections over, the campaign for the Presidency of France between the two top candidates, François Hollande and Nicholas Sarkozy begins under the cloud of most of Europe in economic recession. Just how much the latest news of England slipping back into recession under the weight of the Cameron government’s austerity measures along with increased taxes, remains to be seen but there are signs that it is already having an impact:
With the first round of elections over, the campaign for the Presidency of France between the two top candidates, François Hollande and Nicholas Sarkozy begins under the cloud of most of Europe in economic recession. Just how much the latest news of England slipping back into recession under the weight of the Cameron government’s austerity measures along with increased taxes, remains to be seen but there are signs that it is already having an impact:
To the left: a likely new direction for France and Germany
If a new austerity-sceptic alliance emerges across the Channel, will Cameron and Osborne end up as Europe’s last deflationists?
Quite suddenly, there is talk of change in the eurozone’s economic strategy and, in particular, of the need for urgent action by the European Union to reverse the downward spiral of negative growth and rising unemployment. The likelihood that François Hollande will be elected as president of France next weekend has injected an important note of dissent into the pro-austerity consensus. Even more important than the French elections, however, may be the indications that even the political debate in Germany is now changing its tune.
The opposition German social democratic SPD hopes for election victory in the key state of North Rhine Westphalia on 13 May, as well as in the German general election next year. The SPD has already signalled that it will support the French Socialists in support of an investment-led EU strategy to boost growth and jobs. Moreover, the German social democrats and the German Green party also back the creation of euro-bonds and using the proceeds of a tax on financial transactions to finance a return to growth.
Chancellor Angela Merkel is a bit nervous about a Hollande government:
It is unclear at this time whether next year’s German general election will lead to an SPD/Green coalition government or to a “grand coalition” of the SPD and Chancellor Merkel’s Christian Democrats. But Angela Merkel has already sent some of her top advisers to Paris to explore the proposals of the French Socialists and to see to what extent she and a future President Hollande might be able to salvage a Franco-German partnership in the EU.
The conservative German government is resolutely opposed to any formal re-negotiation of the “stability and governance treaty” which has been cited to justify the crippling austerity measures imposed on Greece and other eurozone “peripheral” economies. But Hollande is now focussing on a series of “additional measures” rather than actual “changes” to the treaty. These additional growth measures would include a major boost to the resources of the European Investment Bank to allow it to put far more capital to work, especially in the hardest-hit economies. Second, the French Socialists would like to see the European stability mechanism given the status of a bank, so that it can receive funding from the European Central Bank and thus be better able to contain any future crisis affecting the euro. Third, they argue for widening the mandate of the ECB so that it is obliged to pursue growth objectives as well as price stability.
Unsurprisingly, a number of sympathetic noises off are being heard from Rome, Madrid and other EU countries, where centre-right governments which are struggling against economic suffocation by obsessive austerityitis.
President Nicholas Sarkozy, who is behind Hollande 54% to 46% in the polls, has said that there would be no coalition with the far right wing National Front Party, whose candidate, Marine Le Pen garnered 17.9% of the vote placing third:
“There will be no pact with the Front National,” he told France Info radio, adding there were too many issues on which they disagreed to imagine giving the party cabinet posts. The Front National has called for France to quit the euro and a hold a referendum on the death penalty, both far from Sarkozy’s manifesto.
“There will be no Front National ministers, but I refuse to demonise men and women who in voting for Marine Le Pen cast a crisis vote, a vote of anger, a vote of suffering and a vote of despair. I have to listen to their message and take them into account, and not think it’s time to hold my nose,” Sarkozy said.
Currently the National Front holds no seats in the French Parliament but hope to change that in the up coming national elections in June.
Geographically, Le Pen has broadened Front National support beyond her father’s heartlands in the south, and polled well in villages and rural constituencies across the country as well as on the outskirts of cities. She did well in the depressed former industrial areas of the north and east, but also saw increases in support in rural areas beyond Bordeaux and in Normandy. The prospect of Front National gains has left Sarkozy’s ruling UMP party, a broad coalition of centre right and rightwing factions, scrapping over what tack to take to hang on to their seats. The party is already divided and facing an internal battle over its future if Sarkozy loses the election
There will obviously be a battle for Le Pen’s 6.4 million voters with the far left accusing Sarkozy of drifting too far to the right, making some ugly comparisons:
The communist paper L’Humanité sparked a row with its front page comparing Sarkozy to Marshal Pétain, the leader of France’s Nazi collaborationist Vichy regime in the 1940s, who was convicted of treason after the second world war.
The paper said Sarkozy’s decision to hold his own Labour Day rally in Paris on 1 May to celebrate what he termed “real” work, as opposed to the traditional, trade-union-led rallies by the left, harked back to a Pétain-style discourse. Pétain – whose motto was “travail, famille, patrie” (work, family, country) – had aimed to reclaim 1 May for the right.
Max Staat wrote: “Sarkozy isn’t Pétain, happily, but the similarities point to the dangers for our country of the president-candidate adopting the theses of the extreme right.”
And you thought American political campaigns were ugly. Fortunately, the election is May 6, eleven days and all campaigning ends on Friday May 4.
Click on image to enlarge
Apr 26 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Eugene Robinson: The Devil We Don’t Know
It may not be the economy, stupid.
Then again, James Carville’s famous maxim about the 1992 presidential campaign might well be valid in 2012. But it’s quite possible that on Election Day, voters’ most urgent concerns-economic or not-will be driven by overseas events that neither President Obama nor his Republican opponent can predict or control. [..]
And if the Carville dictum turns out to be right? Well, stock markets around the world swooned on Monday-not because of anything U.S. officials said or did but because of events in Europe that made investors nervous. The Dutch government fell, after failing to win approval of new austerity measures, while French President Nicolas Sarkozy finished second in his bid for re-election and faces a runoff.
It may be that in 2012 it’s the eurozone crisis, stupid. And there’s nothing Obama or Romney can do about it.
Robert Reich: How Europe’s Double Dip Could Become America’s
Europe is in recession.
Britain’s Office for National Statistics confirmed today (Wednesday) that in the first quarter of this year Britain’s economy shrank .2 percent, after having contracted .3 percent in the fourth quarter of 2011. (Officially, two quarters of shrinkage make a recession). On Monday Spain officially fell into recession, for the second time in three years. Portugal, Italy, and Greece are already basket cases. It seems highly likely France and Germany are also contracting.
Why should we care? Because a recession in the world’s third-largest economy, combined with the current slowdown in the world’s second-largest (China), spells trouble for the world’s largest.
The nation’s largest private prison company, the Corrections Corporation of America, is on a buying spree. With a war chest of $250 million, the corporation, which is listed on the New York Stock Exchange, earlier this year sent letters to 48 states, offering to buy their prisons outright. To ensure their profitability, the corporation insists that it be guaranteed that the prisons be kept at least 90 percent full. Plus, the corporate jailers demand a 20-year management contract, on top of the profits they expect to extract by spending less money per prisoner.
For the last two years, the number of inmates held in state prisons has declined slightly, largely because the states are short on money. Crime, of course, has declined dramatically in the last 20 years, but that has never dampened the states’ appetites for warehousing ever more Black and brown bodies, and the federal prison system is still growing. However, the Corrections Corporation of America believes the economic crisis has created an historic opportunity to become the landlord, as well as the manager, of a big chunk of the American prison gulag.
John Cavanagh and Scott Klinger: Bank CEOs Gain as Millions Lose Dreams, Retirement to Foreclosure
Inside and outside of Wells Fargo’s annual meeting in San Francisco yesterday, thousands of angry protesters decried the bank’s leading role in the loss of millions of American homes to foreclosure.
If you want to know why the protesters are so angry, consider this double standard. For most Americans, retirement security lies in the value of their homes. Millions of these people have been losing that security as the nation’s largest banks have foreclosed on them. Yet the CEOs of these banks are reaping giant pay packages and padding their own retirement security with profits squeezed from ordinary people.
For many American families, a paid-off home is part of the dream of a secure retirement. The roof over their heads has long comprised the largest element of most families’ net worth. The housing crisis brought to us by the country’s biggest bankers has stolen the dreams of the nearly 4 million families who have lost their homes to foreclosure since the housing crisis began in 2007.
Richard (RJ) Eskow: Will a Young Generation’s Dreams Be Rescued — Or Bundled and Sold on Wall Street?
Interest rates for student loans will double on July 1 unless Congress acts. That’s outrageous — but the fiscal abuse of our nation’s young people runs far deeper than that. An entire generation has been trapped into debt servitude and joblessness by the implacable machinery of Wall Street greed. Bank-servile scolds insult the young people of America while the bankers’ economic engines strip-mine their financial future.
Jobless or overextended college graduates aren’t even allowed to declare bankruptcy — a privilege that’s extended to every reckless investor and mismanaged corporation in the nation. Once they finally find work, college graduates face years of garnished wages to repay the loans that funded their often-overpriced educations. If they haven’t repaid that debt by the time they grow old — a very real possibility at the cost of a college education today — they’ll even be forced to surrender part of their Social Security benefits.
That’s indentured servitude.
Mike Lux: K Street and Wall Street in Trouble in 2012
The big news coming out of the Pennsylvania primaries yesterday are that two of K Street’s favorite Capitol Hill Democrats, Tim Holden and Jason Altmire, got upset in races where they had lots more cash than their opponents but still got taken down. The way these races played out should be a big lesson to Democrats who think they can take special interest cash, make pro-special interest votes and still win elections. And with big issues like student loans, tax subsidies for Wall Street and Big Oil, and accountability for the big banks in play the rest of the year, politicians should pay attention.
Holden was an incumbent and his only weakness was that he was forced to run in a more Democratic district than he used to have. Given that he voted with corporate special interests and Republicans a lot of the time — including on the Bush tax cuts and fracking and factory farms — that became a big problem when he faced a progressive challenger named Matt Cartwright. Holden had the support of the Democratic establishment and the monied interests, but Cartwright thumped him.
Apr 26 2012
CISPA: Cybersecurity That Leaves Us All Unsecure
 Here we go again with the right to internet privacy and security for the individual being threatened by the government on behalf of corporations. On November 11 last year, the Cyber Intelligence Sharing and Protection Act was introduced in the House by U.S. Representative Michael Rogers (R-MI) and 111 co-sponsors. The bills supposed purpose would allow the voluntary sharing of attack and threat information between the U.S. government and security cleared technology and manufacturing companies to ensure the security of networks against patterns of attack.
Here we go again with the right to internet privacy and security for the individual being threatened by the government on behalf of corporations. On November 11 last year, the Cyber Intelligence Sharing and Protection Act was introduced in the House by U.S. Representative Michael Rogers (R-MI) and 111 co-sponsors. The bills supposed purpose would allow the voluntary sharing of attack and threat information between the U.S. government and security cleared technology and manufacturing companies to ensure the security of networks against patterns of attack.
What does that mean, you ask? Well, as Rep. Ron Paul (R-TX) explains the bill would allow “both the federal government and private companies to view your private online communications without judicial oversight provided that they do so of course in the name of cyber-security.” Paul calls the CISPA the new SOPA:
CISPA represents an alarming form of corporatism, as it further intertwines government with companies like Google and Facebook. It permits them to hand over your private communications to government officials without a warrant, circumventing well-established federal laws like the Wiretap Act and the Electronic Communications Privacy Act. It also grants them broad immunity from lawsuits for doing so, leaving you without recourse for invasions of privacy. Simply put, CISPA encourages some of our most successful internet companies to act as government spies, sowing distrust of social media and chilling communication in one segment of the world economy where America still leads.
Proponents of CISPA may be well-intentioned, but they unquestionably are leading us toward a national security state rather than a free constitutional republic. Imagine having government-approved employees embedded at Facebook, complete with federal security clearances, serving as conduits for secret information about their American customers. If you believe in privacy and free markets, you should be deeply concerned about the proposed marriage of government intelligence gathering with private, profit-seeking companies. CISPA is Big Brother writ large, putting the resources of private industry to work for the nefarious purpose of spying on the American people. We can only hope the public responds to CISPA as it did to SOPA back in January. I urge you to learn more about the bill by reading a synopsis provided by the Electronic Frontier Foundation on their website at eff.org. I also urge you to call your federal Senators and Representatives and urge them to oppose CISPA and similar bills that attack internet freedom.
This is CISPA (pdf):
CISPA could allow any private company to share vast amounts of sensitive, private data about its customers with the government. CISPA would override all other federal and state privacy laws, and allow a private company to share nearly anything-from the contents of private emails and Internet browsing history to medical, educational and financial records-as long as it “directly pertains to” a “cyber threat,” which is broadly defined. CISPA does not require that data shared with the government be stripped of unnecessary personally-identifiable information. A private company may choose to anonymize the data it shares with the government. However, there is no requirement that it does so-even when personally-identifiable information is unnecessary for cybersecurity measures. For example, emails could be shared with the full names of their authors and recipients. A company could decide to leave the names of its customers in the data it shares with the government merely because it does not want to incur the expense of deleting them. This is contrary to the recommendations of the House Republican Cybersecurity Task Force and other bills to authorize information sharing, which require companies to make a reasonable effort to minimize the sharing of personally-identifiable information. CISPA would allow the government to use collected private information for reasons other than cybersecurity. The government could use any information it receives for “any lawful purpose” besides “regulatory purposes,” so long as the same use can also be justified by cybersecurity or the protection of national security. This would provide no meaningful limit-a government official could easily create a connection to “national security” to justify nearly any type of investigation. CISPA would give Internet Service Providers free rein to monitor the private communications and activities of users on their networks. ISPs would have wide latitude to do anything that can be construed as part of a “cybersecurity system,” regardless of any other privacy or telecommunications law. CISPA would empower the military and the National Security Agency (NSA) to collect information about domestic Internet users. Other information sharing bills would direct private information from domestic sources to civilian agencies, such as the Department of Homeland Security. CISPA contains no such limitation. Instead, the Department of Defense and the NSA could solicit and receive information directly from American companies, about users and systems inside the United States. CISPA places too much faith in private companies, to safeguard their most sensitive customer data from government intrusion. While information sharing would be voluntary under CISPA, the government has a variety of ways to pressure private companies to share large volumes of customer information. With complete legal immunity, private companies have few clear incentives to resist such pressure. There is also no requirement that companies ever tell their customers what they have shared with the government, either before or after the fact. As informed consumers, Americans expect technology companies to have clear privacy policies, telling us exactly how and when the company will use and share our personal data, so that we can make informed choices about which companies have earned our trust and deserve our business.
On Wednesday the White House Office of Management and Budget issues a lengthy statement in opposition to CISPA and a threat to veto the bill:
“H.R. 3523 fails to provide authorities to ensure that the Nation’s core critical infrastructure is protected while repealing important provisions of electronic surveillance law without instituting corresponding privacy, confidentiality, and civil liberties safeguards. […]” “The bill also lacks sufficient limitations on the sharing of personally identifiable information between private entities and does not contain adequate oversight or accountability measures necessary to ensure that the data is used only for appropriate purposes. […]” It would “inappropriately shield companies from any suits where a company’s actions are based on cyber threat information identified, obtained, or shared under this bill, regardless of whether that action otherwise violated Federal criminal law or results in damage or loss of life. […]” And finally, it “effectively treats domestic cybersecurity as an intelligence activity and thus, significantly departs from longstanding efforts to treat the Internet and cyberspace as civilian spheres. […]” “If H.R. 3523 were presented to the President, his senior advisors would recommend that he veto the bill,” OMB said.
h/t to Joan McCarter at Daily Kos for the summery
We at The Stars Hollow Gazette and Docudharma strongly oppose CISPA and urge you to contact your Congress person:
Tell Congress: Keep My Inbox Away From the Government
and to sign the petition:
Apr 26 2012
On This Day In History April 26
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
April 26 is the 116th day of the year (117th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 249 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1986, the world’s worst nuclear power plant accident occurs at the Chernobyl nuclear power station in the Soviet Union. Thirty-two people died and dozens more suffered radiation burns in the opening days of the crisis, but only after Swedish authorities reported the fallout did Soviet authorities reluctantly admit that an accident had occurred.
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant in the Ukrainian SSR (now Ukraine). An explosion and fire released large quantities of radioactive contamination into the atmosphere, which spread over much of Western Russia and Europe. It is considered the worst nuclear power plant accident in history, and is one of only two classified as a level 7 event on the International Nuclear Event Scale (the other being the Fukushima I nuclear incident, which is considered far less serious and has caused no direct deaths). The battle to contain the contamination and avert a greater catastrophe ultimately involved over 500,000 workers and cost an estimated 18 billion rubles, crippling the Soviet economy.
The disaster began during a systems test on 26 April 1986 at reactor number four of the Chernobyl plant, which is near the town of Pripyat. There was a sudden power output surge, and when an emergency shutdown was attempted, a more extreme spike in power output occurred, which led to a reactor vessel rupture and a series of explosions. These events exposed the graphite moderator of the reactor to air, causing it to ignite. The resulting fire sent a plume of highly radioactive smoke fallout into the atmosphere and over an extensive geographical area, including Pripyat. The plume drifted over large parts of the western Soviet Union and Europe. From 1986 to 2000, 350,400 people were evacuated and resettled from the most severely contaminated areas of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. According to official post-Soviet data, about 60% of the fallout landed in Belarus.
The accident raised concerns about the safety of the Soviet nuclear power industry, as well as nuclear power in general, slowing its expansion for a number of years and forcing the Soviet government to become less secretive about its procedures.
(Click on image to enlarge) Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus have been burdened with the continuing and substantial decontamination and health care costs of the Chernobyl accident. Thirty one deaths are directly attributed to the accident, all among the reactor staff and emergency workers. A UNSCEAR report places the total confirmed deaths from radiation at 64 as of 2008. Estimates of the number of deaths potentially resulting from the accident vary enormously: the World Health Organization (WHO) suggest it could reach 4,000; a Greenpeace report puts this figure at 200,000 or more; a Russian publication, Chernobyl, concludes that 985,000 excess deaths occurred between 1986 and 2004 as a result of radioactive contamination.
After the explosion at reactor four, the remaining three reactors at the power plant continued to operate. In 1991, reactor two suffered a major fire, and was subsequently decommissioned. In November 1996, reactor one was shut down, followed by reactor three on December 15, 2000, making good on a promise by Ukrainian president Leonid Kuchma that the entire plant would be closed.
Even after the last reactor shutdown, people continue to work at the Chernobyl plant until reactor units 1, 2, and 3 are totally decommissioned, which is expected to take years. The first stage of decommissioning is the removal of the highly radioactive spent nuclear fuel, which is placed in deep water cooling ponds. However, storage facilities for this are not suitable for long term containment, and those on site do not have the capacity for all the spent fuel from units 1, 2 and 3. A second facility is planned for construction that will use dry storage technology suitable for long term storage and have the required capacity.
Removal of uncontaminated equipment has begun at unit 1 and this work could be complete by 2020-2022.
The remains of reactor unit 4 will remain radioactive for some time. The isotope responsible for the majority of the external gamma radiation dose at the site is Caesium-137 which has a half-life of about 30 years. It is likely that with no further decontamination work the gamma ray dosage at the site will return to background levels in about three hundred years. However, as most of the alpha emitters are longer lived, the soil and many surfaces in and around the plant are likely to be contaminated with transuranic metals such as plutonium and americium, which have much longer half-lives. It is planned that the reactor buildings will be disassembled as soon as it is radiologically safe to do so.
Apr 25 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
Wednesday is Ladies’ Day
Ilyse Hogue: An Unlikely Coalition in New York Pushes Cuomo on Public Finance
These words, uttered by Governor Andrew Cuomo at his State of the State address in January, could have been discounted as a rhetorical nod to a base issue by a Democratic governor a year into his four-year term. That’s the risk of a system where money in politics feels as pervasive as sand on the beach: its ubiquity creates a dangerous inertia that prevents citizens from seizing real opportunities for change. But thanks to a coalition of New Yorkers dedicated to elevating and actualizing Governor Cuomo’s pledge, this year could not only rewrite the rules in New York but also change the risk calculation on engagement for the entire country.
As the Supreme Court has chipped away at the protections in McCain-Feingold (a k a the Bi-Partisan Campaign Reform Act) and Citizens United has opened the flood gates to corporate money in the political system, the collective frustration has risen to an astonishing 83 percent of Americans who believe that there’s too much money in politics. But despite the rare across-the-board consensus, federal policy solutions have been at a standstill. The vicious cycle that gives rise to big-money candidates has produced overwhelmingly negative incentives to stepping out on government accountability. That gives wealthy and corporate interests a virtual lock on the status quo.
New York’s public finance legislation, if it comes to a vote in June, could be the beginning of the end of that dynamic, which is why it’s worth exploring the key elements that make this issue viable again.
Katrina vanden Heuvel: A vote for universal registration
I recently visited Russia, where a mild-mannered historian from the city of Astrakhan, Oleg Shein, is on a hunger strike protesting a stolen mayoral election he believes he won. But as Russia starves for free and fair elections, Republicans across the United States are starving our democracy – and too few have noticed. And their furious assault on voting rights is no less destructive to democracy than the vote-rigging we deplore in Russia.
Over the past year, Republican legislators in 34 states have proposed legislation that would drastically restrict voting for an estimated 5 million eligible voters. Seven states have passed laws requiring voters to show photo ID – which more than one in 10 Americans lacks – and dozens of others have eliminated early voting, disenfranchised ex-felons or limited the ability of civic organizations to register voters. The consequences are clear in Texas, for example, where you can now register to vote with a handgun license but not a college ID.
Under the pretext of parental ‘choice’, the right is using vouchers to establish religion in public education – with Romney’s blessing
“Choice” is such a nice word that everybody wants to have it on their side.
“Choice” is also a fuzzy word, which may be why Mitt Romney is willing to call himself a supporter of “school choice”. In the strange language of education politics, “choice” sometimes means advocating the partial privatization of school systems through charter schools – which Romney supports. It can also indicate support for voucher programs, which is another thing altogether – and which Romney is said also to support.
Charter schools are constrained by the same laws and policies that, for example, prohibit public schools from endorsing religion. Vouchers, on the other hand, allow parents to use public money to pay for private, mostly religious schools that are largely unaccountable to the public. So, for example, a voucher school may use your taxpayer dollars to teach its students that the earth is 6,000 years old. And a number of such schools now do just that.
Michele Chen: Labor Action and Inaction in Colombia Free Trade Deal
As the media swarmed over the scandal surrounding the Secret Service’s alleged carousing with prostitutes in Colombia, another questionable financial transaction slipped quietly through the backdoor of hemispheric diplomacy.
While officials convened at the Summit of the Americas in Cartagena earlier this month, the White House put the finishing touches on another free trade agreement, aimed at liberalizing markets in Colombia and the U.S. The deal has faced vocal resistance from labor and human rights groups in both countries, who argue that the agreement would effectively condone violence against activists and economic oppression. But for the governments looking to build economic ties, the fears raised by civil society groups were just background noise. The Obama administration tried to put the lid on the opposition by tacking on labor policies to address anti-labor violence and other abuses.
Sarah Jerving: ALEC’s Vision of Pre-Empting EPA Coal Ash Regs Passes the House
The U.S. House of Representatives passed an amendment on April 18 to the Surface Transportation Extension Act of 2012 (HR 4348) that would effectively pre-empt the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) from regulating coal ash, the waste from coal burning plants. About 140 million tons of coal ash are produced by power plants in the United States each year. There are about 1,000 active coal ash storage sites across the country.
According to the EPA, the ash contains concentrations of arsenic, boron, cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury and other metals, but the coal industry has claimed there is less mercury in the ash than in a fluorescent light bulb. However, the EPA found in 2010 that the cancer risk from arsenic near some unlined coal ash ponds was one in 50 — 2,000 times the agency’s regulatory goal. Additionally, researchers from the Environmental Integrity Project, Earthjustice, and Sierra Club have documented water contamination from coal ash sites in 186 locations. The new bill would strip the EPA’s authority to regulate the ash and hand it over to the states.
Jessica Valenti: Did Conservative Sting Operatives Target Planned Parenthood-Again?
After a series of odd visits by patients asking questions about sex-selective abortions, Planned Parenthood has determined that their centers are likely the target of another undercover video “sting” operation.
In a post on RH Reality Check, Planned Parenthood’s Vice President of Education Leslie Kantor and Senior Medical Adviser Dr. Carolyn Westhoff wrote that they anticipate the group-presumably Live Action, which has targeted Planned Parenthood in the past – “likely in coordination with a broad range of anti-choice leaders, will soon launch a propaganda campaign with the goal of discrediting Planned Parenthood.”
According to the Huffington Post, Planned Parenthood clinics in at least eleven states over the last few weeks have been the target of “patients” coming in asking a series of questions about finding out the gender of their fetus, and indicating that they want to terminate the pregnancy if it’s a girl.
Cecillia Wang: Will Americans Tolerate Laws that Encourage Racial Profiling?
When the Supreme Court hears arguments on April 25 challenging Arizona’s notorious anti-immigrant law, S.B. 1070, it will tackle the legal question of whether states can create a patchwork of separate immigration laws, beyond the control of the U.S. government.
But laws like S.B. 1070 pose even more fundamental questions for our nation. As Americans, will we tolerate discriminatory laws that encourage racial profiling? Or will we choose fairness and equality over discrimination and a police state that reaches into our personal lives?
We are used to saying that we live in a free country. But S.B. 1070 and its ilk threaten our cherished freedoms. Arizonans are not the only ones at risk. Alabama, Georgia, Indiana, South Carolina and Utah have passed similar laws. If the courts allow them to go forward, everyone in these states will always need to carry identity papers to guard against police intrusions.
Apr 25 2012
On This Day In History April 25
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
April 25 is the 115th day of the year (116th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 250 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1859, ground broken is for Suez Canal
At Port Said, Egypt, ground is broken for the Suez Canal, an artificial waterway intended to stretch 101 miles across the isthmus of Suez and connect the Mediterranean and the Red seas. Ferdinand de Lesseps, the French diplomat who organized the colossal undertaking, delivered the pickax blow that inaugurated construction.
Artificial canals have been built on the Suez region, which connects the continents of Asia and Africa, since ancient times. Under the Ptolemaic rulers of Egypt, a channel connected the Bitter Lakes to the Red Sea, and a canal reached northward from Lake Timsah as far as the Nile River. These canals fell into disrepair or were intentionally destroyed for military reasons. As early as the 15th century, Europeans speculated about building a canal across the Suez, which would allow traders to sail from the Mediterranean to the Indian Ocean via the Red Sea, rather than having to sail the great distance around Africa’s Cape of Good Hope.
The Suez Canal, when first built, was 164 km (102 mi) long and 8 m (26 ft) deep. After multiple enlargements, the canal is 193.30 km (120.11 mi) long, 24 m (79 ft) deep, and 205 metres (673 ft) wide as of 2010. It consists of the northern access channel of 22 km/14 mi, the canal itself of 162.25 km/100.82 mi and of the southern access channel of 9 km/5.6 mi.
It is single-lane with passing places in Ballah By-Pass and in the Great Bitter Lake. It contains no locks; seawater flows freely through the canal. In general, the Canal north of the Bitter Lakes flows north in winter and south in summer. The current south of the lakes changes with the tide at Suez.
The canal is owned and maintained by the Suez Canal Authority (SCA) of the Arab Republic of Egypt. Under international treaty, it may be used “in time of war as in time of peace, by every vessel of commerce or of war, without distinction of flag.”
Construction by Suez Canal Company
In 1854 and 1856 Ferdinand de Lesseps obtained a concession from Sa’id Pasha, the Khedive of Egypt and Sudan, to create a company to construct a canal open to ships of all nations. The company was to operate the canal for 99 years from its opening. De Lesseps had used his friendly relationship with Sa’id, which he had developed while he was a French diplomat during the 1830s. As stipulated in the concessions, Lesseps convened the International Commission for the piercing of the isthmus of Suez (Commission Internationale pour le percement de l’isthme des Suez) consisting of thirteen experts from seven countries, among them McClean, President of the Institution of Civil Engineers in London, and again Negrelli, to examine the plans of Linant de Bellefonds and to advise on the feasibility of and on the best route for the canal. After surveys and analyses in Egypt and discussions in Paris on various aspects of the canal, where many of Negrelli’s ideas prevailed, the commission produced a final unanimous report in December 1856 containing a detailed description of the canal complete with plans and profiles. The Suez Canal Company (Compagnie Universelle du Canal Maritime de Suez) came into being on 15 December 1858 and work started on the shore of the future Port Said on April 25, 1859.
The excavation took some 10 years using forced labour (Corvée) of Egyptian workers during a certain period. Some sources estimate that over 30,000 people were working on the canal at any given period, that altogether more than 1.5 million people from various countries were employed, and that thousands of laborers died on the project.
The British government had opposed the project of the canal from the outset to its completion. As one of the diplomatic moves against the canal, it disapproved the use the slave labor of forced workers on the canal. The British Empire was the major global naval force and officially condemned the forced work and sent armed bedouins to start a revolt among workers. Involuntary labour on the project ceased, and the viceroy condemned the Corvée, halting the project.
Angered by the British opportunism, de Lesseps sent a letter to the British government remarking on the British lack of remorse a few years earlier when forced workers died in similar conditions building the British railway in Egypt.
Initially international opinion was skeptical and Suez Canal Company shares did not sell well overseas. Britain, the United States, Austria, and Russia did not buy any significant number of shares. All French shares were quickly sold in France
Apr 24 2012
NSA: Every Step You Take, We’ll be Watching You
National Security Agency whistleblower William Binney reveals he believes domestic surveillance has become more expansive under President Obama than President George W. Bush. He estimates the NSA has assembled 20 trillion “transactions” – phone calls, emails and other forms of data – from Americans. This likely includes copies of almost all of the emails sent and received from most people living in the United States. Binney talks about Section 215 of the USA PATRIOT Act and challenges NSA Director Keith Alexander’s assertion that the NSA is not intercepting information about U.S. citizens
This interview is part of a 4-part special. Click here to see segment 1, 2, and 4. [includes rush transcript]
Guests:
William Binney, served in the NSA for over 30 years, including a time as director of the NSA’s World Geopolitical and Military Analysis Reporting Group. Since retiring from the NSA in 2001, he has warned that the NSA’s data-mining program has become so vast that it could “create an Orwellian state.”
Jacob Appelbaum, a computer security researcher who has volunteered with WikiLeaks. He is a developer and advocate for the Tor Project, a network enabling its users to communicate anonymously on the internet.
Laura Poitras, an award-winning documentary filmmaker and producer. She is working on the third part of a trilogy of films about America post-9/11. The first film was My Country, My Country,” and the second was The Oath.
by George Washington at naked capitalism
Senator Church’s Prophetic Warning
Senator Frank Church – who chaired the famous “Church Committee” into the unlawful FBI Cointel program, and who chaired the Senate Foreign Relations Committee – said in 1975:
“Th[e National Security Agency’s] capability at any time could be turned around on the American people, and no American would have any privacy left, such is the capability to monitor everything: telephone conversations, telegrams, it doesn’t matter. There would be no place to hide. [If a dictator ever took over, the N.S.A.] could enable it to impose total tyranny, and there would be no way to fight back.“
Now, the NSA is building a $2 billion dollar facility in Utah which will use the world’s most powerful supercomputer to monitor virtually all phone calls, emails, internet usage, purchases and rentals, break all encryption, and then store everyone’s data permanently.
The former head of the program for the NSA recently held his thumb and forefinger close together, and said:
We are, like, that far from a turnkey totalitarian state
So Senator Church’s warning was prophetic.
George goes on to extensively discuss:
This started in the 1970’s during the Ford administration when Dick Cheney and Donald Rumseld pushed for wiretaps without approval by a judge. It has expanded under each successive president, including the present occupant of the White House who was elected after lying about “fixing” FISA and the Patriot Act.
Apr 24 2012
Punting the Pundits
“Punting the Pundits” is an Open Thread. It is a selection of editorials and opinions from around the news medium and the internet blogs. The intent is to provide a forum for your reactions and opinions, not just to the opinions presented, but to what ever you find important.
Thanks to ek hornbeck, click on the link and you can access all the past “Punting the Pundits”.
New York Times Editorial: France Votes Its Discontents
The first-round vote in the French presidential election produced a curious bi-directional backlash – from the left against the policies of austerity and from the right against immigration. The final round, which will be held on May 6, is likely to be important for all of Europe.
Sunday’s vote produced two front-runners: François Hollande, the Socialist Party challenger who received more than 28 percent of the vote; and President Nicolas Sarkozy, who got about 27 percent. Since neither got a majority, they will face each other in a runoff. [..]
A second-round victory by Mr. Hollande would signal a major change in fiscal direction for France and, by extension, for the entire 17-nation euro zone. A cautious moderate on most issues, and certainly not a socialist in the historic meaning of that term, Mr. Hollande, nevertheless, recognizes that the German-inspired austerity policies Mr. Sarkozy favors are not succeeding.
Eugene Robinson: Could overseas events drive the 2012 election?
It may not be the economy, stupid.
Then again, James Carville’s famous maxim about the 1992 presidential campaign might well be valid in 2012. But it’s quite possible that on Election Day, voters’ most urgent concerns – economic or not – will be driven by overseas events that neither President Obama nor his Republican opponent can predict or control. [..]
But it might be more pertinent to ask, for example, what the North Korean news agency meant Monday with its threat to reduce parts of Seoul to ash with a military attack “by unprecedented peculiar means and methods of our own style.”
North Korea’s apocalyptic rhetoric can usually be written off as bluster. But the Stalinist dynasty in charge of the world’s most isolated country has an inexperienced young leader whose first attempt to cover himself in glory – testing a provocative new long-range missile – was a humiliating failure. Could Kim Jong Eun actually be thinking the unthinkable?
One of my responsibilities when I was head of corporate communications at Cigna was to help ensure that the company’s annual meeting of shareholders ran smoothly and, if at all possible, attracted no negative publicity.
I always dreaded the annual meeting because you really never knew if one or more disgruntled shareholders might show up and ask rude questions of the CEO. But during all of my years of helping plan those meetings, we had an unblemished string of non-events. We considered the meetings marathons if they lasted more than 15 minutes. Most of them were over-long before then. Over the course of 10 years, I only recall two reporters who felt compelled to attend, and one of them got stuck in traffic and missed the whole thing.
Some of my peers at other health insurers were not that lucky, but relatively few of the big-profit insurers have had to cope with contentious shareholder meetings.
It is clear those days are over.
Dean Baker: Killing the Messenger: The Downsizing and Death of the Postal Service
It is fashionable to think of the postal service as an antiquated relic of a different era in the same way that all right-thinking people regarded standard 30-year fixed rate mortgages as old-fashioned at the peak of the housing bubble. Many of the same people who assured us that we could effectively manage risk through mortgage securitization are now anxious to hand the postal service a death sentence.
Death, or at least a near death experience, is the likely outcome of S.1789, the bill to downsize the Postal Service that the Senate is scheduled to vote on Tuesday night. The bill would end Saturday delivery and also raise the target delivery time from 1-2 days to 2-3 days.
The idea is that people won’t generally care if a letter takes 3 days rather than 2 to reach its destination. While that is probably true, this will certainly increase the frequency with which a letter takes a week or more to reach its destination, and people do care about and remember these instances. This additional delay is likely to seriously reduce the standing of the Postal Service in most people’s eyes, leading to a further erosion of business.
Ari Melber: Media Favored Horserace Over Issues in Presidential Primary
For all the griping about media bias in politics, good data is in short supply. Every four years, however, the nonpartisan Pew Research Center releases exhaustive, quantitative reports on how the press covers the presidential campaign. Their new report, out Monday, shows that the largest bias this year did not favor an ideology or candidate-though Santorum never got much love-but favored the coverage of the horserace and personal issues over public policy.
The press covered the horserace seven times more than domestic issues in the GOP primary. [..]
While it’s hard to see what voters are supposed to base their decisions on if most coverage is about tactics, not the actual issues in the race, Pew notes that 2012 was actually better on this score than last cycle. Then, strategy made up a whopping 80 percent of press coverage about the GOP field, and 78 percent for the Democrats. That may have been because the 2008 race had even more drama between the candidates.
Paul Buchheit: The Middle Class Hasn’t Disappeared. It’s Just Sliding Toward the Bottom
It used to be that the average American resided halfway between two extremes:
Steven Schwarzman’s home was being partially replicated in a Park Avenue hall for his gala $5 million 60th birthday party. The guest of honor’s full-length portrait greeted the invitees as they proceeded past rows of orchids and palm trees to the dining area, where they feasted on lobster, filet mignon, baked Alaska, and the finest of wines. Martin Short provided the laughs, and the music came compliments of Marvin Hamlisch, Patti LaBelle, and Rod Stewart.
Eloise Pittman’s home had been purchased in the 1950s by her mother, who washed dishes to pay off the mortgage. In 1985 the younger Ms. Pittman, a schoolteacher, went to Chase Bank and took out a loan on the house. It was a predatory loan with balloon payments, and Ms. Pittman was forced to borrow more and more money to keep from defaulting. When she died in November 2011, she was $400,000 in debt. A week after her death her family received an eviction notice.
There’s no ‘average’ anymore, in the sense of a normal curve with most of the people and most of the money in the middle.
Today, 400 individuals have as much wealth as an entire HALF of America.
Apr 24 2012
On This Day In History April 24
This is your morning Open Thread. Pour your favorite beverage and review the past and comment on the future.
Find the past “On This Day in History” here.
(Click on images to enlarge)
April 24 is the 114th day of the year (115th in leap years) in the Gregorian calendar. There are 251 days remaining until the end of the year.
On this day in 1916, Easter Rebellion begins.
On Easter Monday in Dublin, the Irish Republican Brotherhood, a secret organization of Irish nationalists led by Patrick Pearse, launches the so-called Easter Rebellion, an armed uprising against British rule. Assisted by militant Irish socialists under James Connolly, Pearse and his fellow Republicans rioted and attacked British provincial government headquarters across Dublin and seized the Irish capital’s General Post Office. Following these successes, they proclaimed the independence of Ireland, which had been under the repressive thumb of the United Kingdom for centuries, and by the next morning were in control of much of the city. Later that day, however, British authorities launched a counteroffensive, and by April 29 the uprising had been crushed. Nevertheless, the Easter Rebellion is considered a significant marker on the road to establishing an independent Irish republic.
Following the uprising, Pearse and 14 other nationalist leaders were executed for their participation and held up as martyrs by many in Ireland. There was little love lost among most Irish people for the British, who had enacted a series of harsh anti-Catholic restrictions, the Penal Laws, in the 18th century, and then let 1.5 million Irish starve during the Potato Famine of 1845-1848. Armed protest continued after the Easter Rebellion and in 1921, 26 of Ireland’s 32 counties won independence with the declaration of the Irish Free State. The Free State became an independent republic in 1949. However, six northeastern counties of the Emerald Isle remained part of the United Kingdom, prompting some nationalists to reorganize themselves into the Irish Republican Army (IRA) to continue their struggle for full Irish independence.
The Act of Union 1801 united the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland, abolishing the Irish Parliament and giving Ireland representation at Westminster. From early on, many Irish nationalists opposed the union and what was seen as the exploitation of the country.
Opposition took various forms: constitutional (the Repeal Association; the Home Rule League), social (disestablishment of the Church of Ireland; the Land League) and revolutionary (Rebellion of 1848; Fenian Rising). Constitutional nationalism enjoyed its greatest success in the 1880s and 1890s when the Irish Parliamentary Party under Charles Stewart Parnell succeeded in having two Home Rule bills introduced by the Liberal government of William Ewart Gladstone, though both failed. The First Home Rule Bill of 1886 was defeated in the House of Commons, while the Second Home Rule Bill of 1893 was passed by the Commons but rejected by the House of Lords. After the fall of Parnell, younger and more radical nationalists became disillusioned with parliamentary politics and turned towards more extreme forms of separatism. The Gaelic Athletic Association, the Gaelic League and the cultural revival under W. B. Yeats and Lady Augusta Gregory, together with the new political thinking of Arthur Griffith expressed in his newspaper Sinn Féin and the organisations the National Council and the Sinn Féin League led to the identification of Irish people with the concept of a Gaelic nation and culture, completely independent of Britain. This was sometimes referred to by the generic term Sinn Féin.
The Third Home Rule Bill was introduced by British Prime Minister H. H. Asquith in 1912. The Irish Unionists, led by Sir Edward Carson, opposed home rule in the light of what they saw as an impending Roman Catholic-dominated Dublin government. They formed the Ulster Volunteer Force on 13 January 1913.
The Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) saw an opportunity to create an armed organisation to advance its own ends, and on 25 November 1913 the Irish Volunteers, whose stated object was “to secure and to maintain the rights and liberties common to all the people of Ireland”, was formed. Its leader was Eoin MacNeill, who was not an IRB member. A Provisional Committee was formed that included people with a wide range of political views, and the Volunteers’ ranks were open to “all able-bodied Irishmen without distinction of creed, politics or social group.” Another militant group, the Irish Citizen Army, was formed by trade unionists as a result of the Dublin Lockout of that year. However, the increasing militarisation of Irish politics was overshadowed soon after by the outbreak of a larger conflict-the First World War and Ireland’s involvement in the conflict.

Recent Comments